| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
 |
氯化钠
CAS:7647-14-5 |
|
 |
甲醛
CAS:50-00-0 |
|
 |
冰醋酸
CAS:64-19-7 |
|
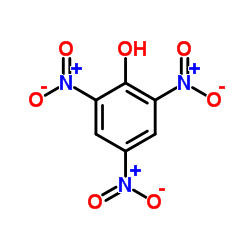 |
苦味酸
CAS:88-89-1 |
|
 |
氯化钠-35cl
CAS:20510-55-8 |
|
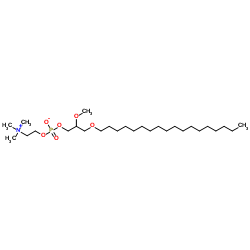 |
依地芬
CAS:70641-51-9 |
|
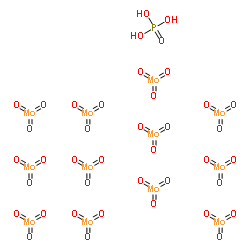 |
磷钼酸水合物
CAS:51429-74-4 |
|
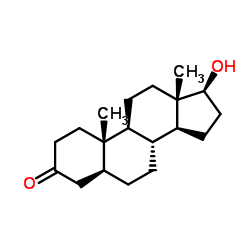 |
雄诺龙
CAS:521-18-6 |
|
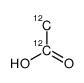 |
乙酸-12C2
CAS:1173022-32-6 |
|
 |
3-氨基-9-乙基咔唑
CAS:132-32-1 |