| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
 |
氯化锰
CAS:7773-01-5 |
|
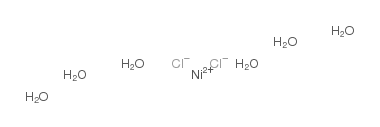 |
氯化镍六水合物
CAS:7791-20-0 |
|
 |
氯化镍
CAS:7718-54-9 |
|
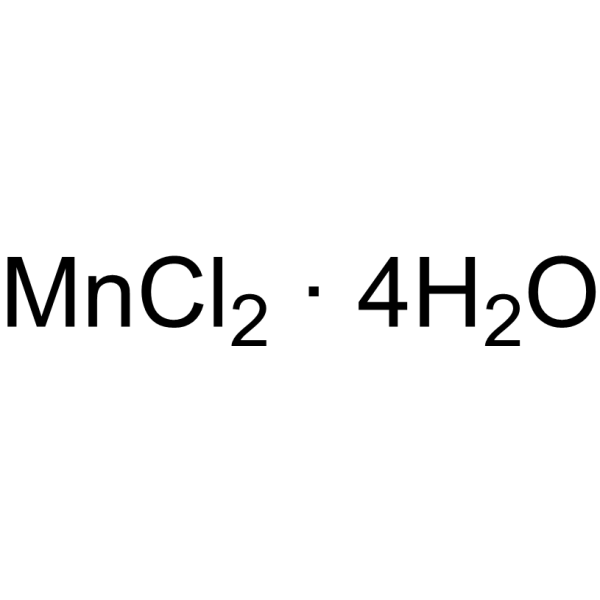 |
氯化锰,四水合物
CAS:13446-34-9 |
|
 |
氯化镍(II) 水合物
CAS:69098-15-3 |