| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
 |
氢氧化钠
CAS:1310-73-2 |
|
 |
3-乙基-2,4-戊烷二酮
CAS:1540-34-7 |
|
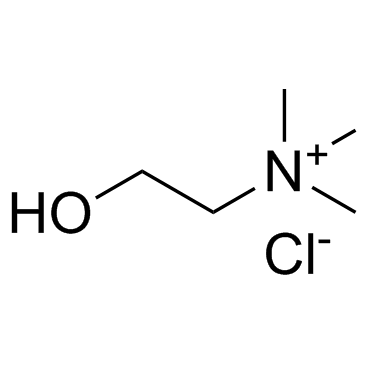 |
氯化胆碱
CAS:67-48-1 |
|
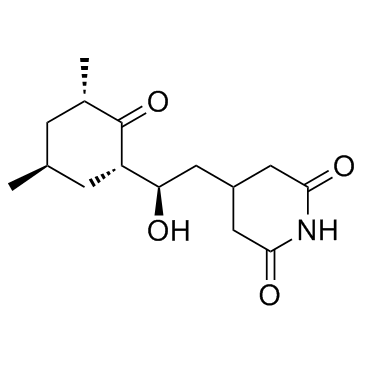 |
放线菌酮
CAS:66-81-9 |
|
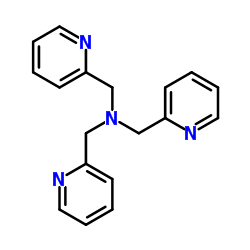 |
三(2-吡啶甲基)胺
CAS:16858-01-8 |
|
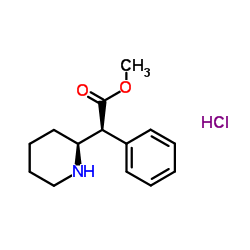 |
盐酸哌甲酯
CAS:298-59-9 |