| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
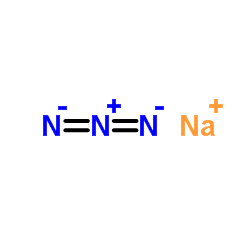 |
叠氮化钠
CAS:26628-22-8 |
|
 |
氯化钠
CAS:7647-14-5 |
|
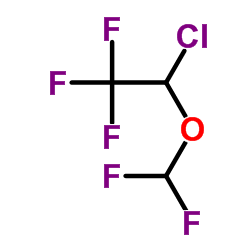 |
异氟醚
CAS:26675-46-7 |
|
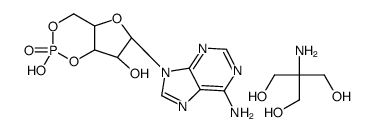 |
腺苷3',5'-环单磷酸三羟甲基氨基甲烷盐
CAS:102029-77-6 |
|
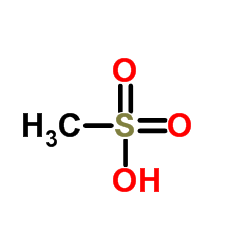 |
甲基磺酸
CAS:75-75-2 |
|
 |
曲拉通X-100
CAS:9002-93-1 |
|
 |
氯化钠-35cl
CAS:20510-55-8 |
|
 |
D-赖氨酸
CAS:923-27-3 |
|
 |
4',6-二脒基-2-苯基吲哚二盐酸盐
CAS:28718-90-3 |
|
 |
环磷酸腺苷
CAS:60-92-4 |