| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
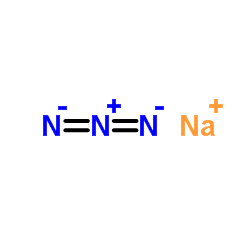 |
叠氮化钠
CAS:26628-22-8 |
|
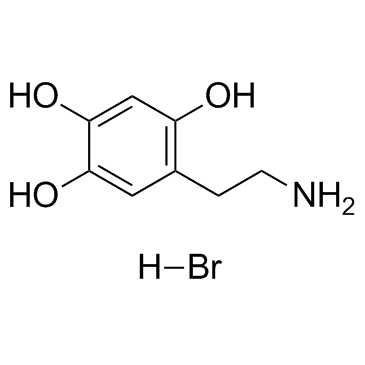 |
6-羟基多巴胺氢溴酸盐
CAS:636-00-0 |
|
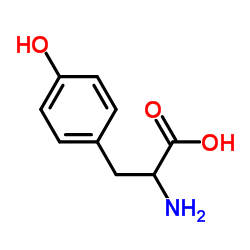 |
DL-酪氨酸
CAS:556-03-6 |