Should nicorandil infusion be adapted in dialysis-dependent patients undergoing continuous renal replacement therapy after cardiac surgery?
Norihisa Yasuda, Koji Goto, Ryo Shitomi, Yoshifumi Ohchi, Takakuni Abe, Shunsuke Yamamoto, Seigo Hidaka, Takayuki Noguchi
文献索引:Artif. Organs 37(3) , 319-22, (2013)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
In this report, we studied whether plasma concentration of nicorandil is maintained effectively and safely in dialysis-dependent patients with stage 5 chronic kidney disease (CKD5D) undergoing continuous renal replacement therapy (CRRT). Participants consisted of 10 patients undergoing CRRT after cardiac surgery. CRRT was performed with an effluent flow rate of either 600 mL/h (low-flow group; n = 5) or 1800 mL/h (high-flow group; n = 5). Nicorandil was infused intravenously at 0.1 mg/kg/h for more than 15 h starting 8 h before and 7 h after the start of CRRT. Plasma nicorandil concentrations were measured from arterial blood lines 1 h before and 7 h after CRRT initiation. Nicorandil clearance by CRRT was also calculated 1 h after CRRT initiation. Nicorandil plasma concentrations before and 7 h after CRRT initiation were 68.0 ng/mL and 74.6 ng/mL, respectively. Nicorandil clearance 1 h after CRRT initiation was 20.2 mL/min. Increasing the effluent flow rate from 600 mL/h to 1800 mL/h tended to increase nicorandil clearance. When nicorandil was infused intravenously during CRRT at 0.1 mg/kg/h in patients with CKD5D, plasma nicorandil concentrations were maintained within an effective concentration range.© 2012, Copyright the Authors. Artificial Organs © 2012, International Center for Artificial Organs and Transplantation and Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
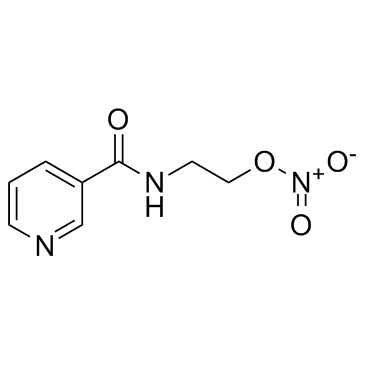 |
尼可地尔
CAS:65141-46-0 |
C8H9N3O4 |
|
Leg ulcers associated with nicorandil are possibly underdiag...
2013-03-01 [Clin. Exp. Dermatol. 38(2) , 193-4, (2013)] |
|
Treating stable angina - is there a NICE way towards an inte...
2012-07-01 [Int. J. Clin. Pract. 66(7) , 614-8, (2012)] |
|
Peristomal ulceration caused by nicorandil.
2009-01-01 [Clin. Exp. Dermatol. 34(1) , 87-8, (2009)] |
|
Nicorandil-associated perianal ulceration: a case series of ...
2006-01-01 [Br. J. Dermatol. 154(1) , 199-200, (2006)] |
|
Nicorandil-associated perianal ulceration with prominent ela...
2005-06-01 [Br. J. Dermatol. 152(6) , 1360-1, (2005)] |