| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
 |
盐酸
CAS:7647-01-0 |
|
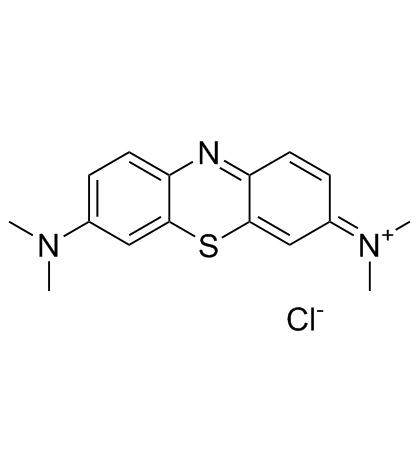 |
亚甲基蓝
CAS:61-73-4 |
|
 |
曙红Y(水溶)
CAS:17372-87-1 |
|
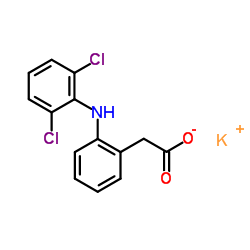 |
双氯芬酸钾
CAS:15307-81-0 |
|
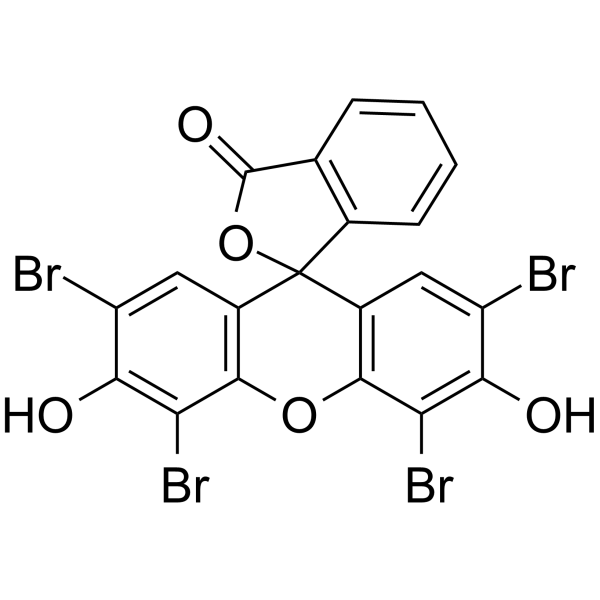 |
曙红Y(醇溶)
CAS:15086-94-9 |
|
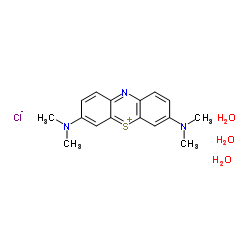 |
亚甲基蓝
CAS:7220-79-3 |
|
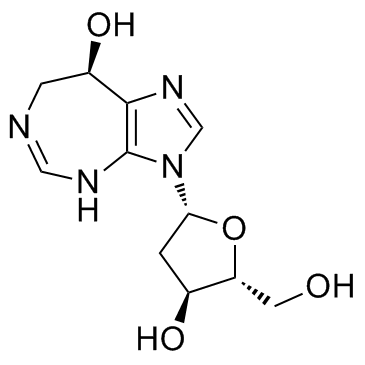 |
喷司他丁
CAS:53910-25-1 |
|
 |
乙二胺四乙酸
CAS:60-00-4 |
|
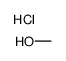 |
氯化氢甲醇溶液
CAS:132228-87-6 |