| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
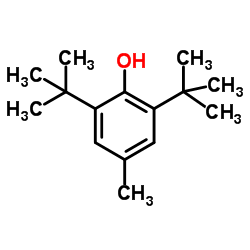 |
抗氧剂BHT
CAS:128-37-0 |
|
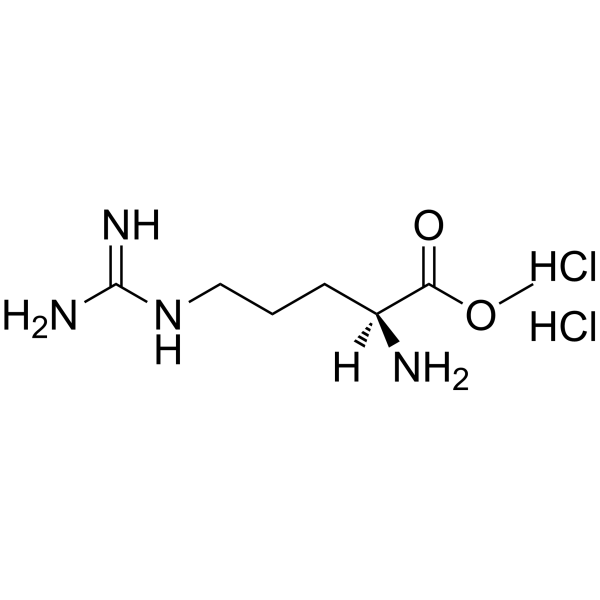 |
L-精氨酸甲酯二盐酸盐
CAS:26340-89-6 |
|
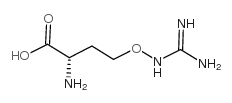 |
L-刀豆氨酸
CAS:543-38-4 |