| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
 |
甲酸
CAS:64-18-6 |
|
 |
乙腈
CAS:75-05-8 |
|
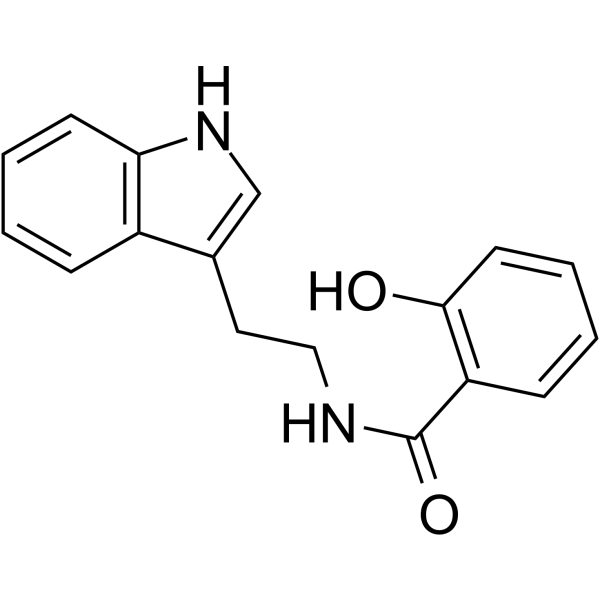 |
N-水杨酰色胺
CAS:31384-98-2 |
|
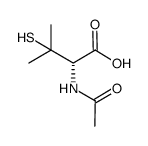 |
N-乙酰基-D-青霉胺
CAS:15537-71-0 |
|
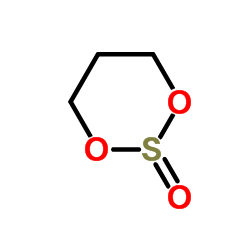 |
亚硫酸丙烯酯
CAS:4176-55-0 |