| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
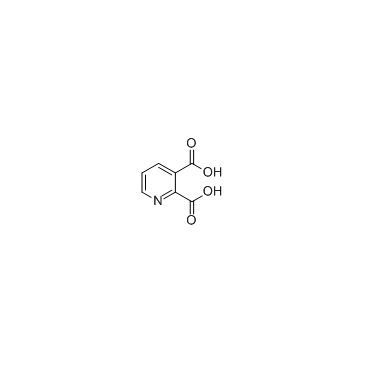 |
吡啶-2,3-二羧酸
CAS:89-00-9 |
|
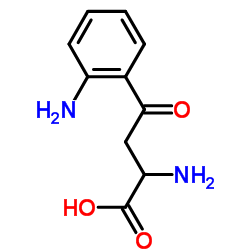 |
犬尿素
CAS:343-65-7 |
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
 |
吡啶-2,3-二羧酸
CAS:89-00-9 |
|
 |
犬尿素
CAS:343-65-7 |