| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
 |
硼氢化钠
CAS:16940-66-2 |
|
 |
氢氧化钠
CAS:1310-73-2 |
|
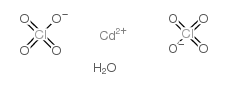 |
高氯酸镉
CAS:79490-00-9 |
|
 |
碲粉
CAS:13494-80-9 |
|
 |
3-乙基-2,4-戊烷二酮
CAS:1540-34-7 |
|
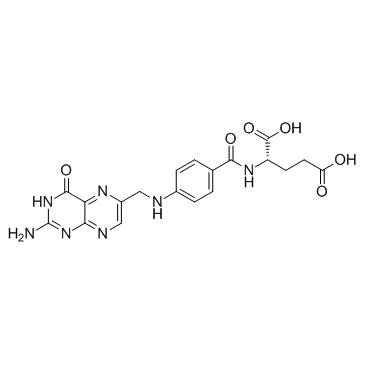 |
叶酸
CAS:59-30-3 |
|
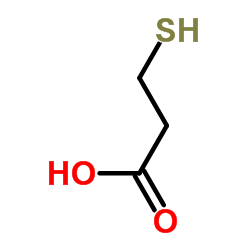 |
3-巯基丙酸
CAS:107-96-0 |