| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
 |
硼氢化钠
CAS:16940-66-2 |
|
 |
盐酸
CAS:7647-01-0 |
|
 |
氢氧化钠
CAS:1310-73-2 |
|
 |
氯化钠
CAS:7647-14-5 |
|
 |
3-乙基-2,4-戊烷二酮
CAS:1540-34-7 |
|
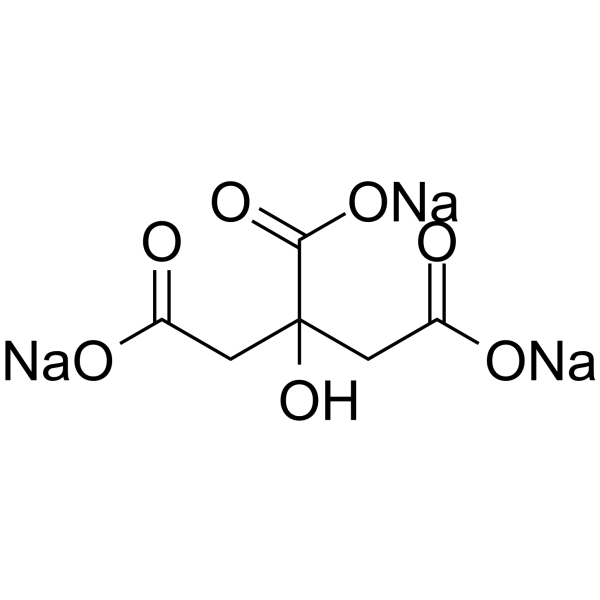 |
柠檬酸钠
CAS:68-04-2 |
|
 |
氯化钠-35cl
CAS:20510-55-8 |
|
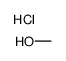 |
氯化氢甲醇溶液
CAS:132228-87-6 |
|
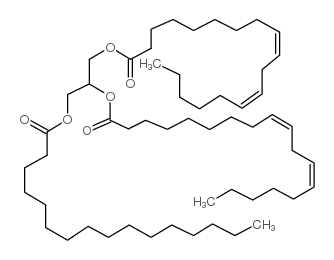 |
1,2亚油酸-3-棕榈酸甘油酯
CAS:2190-15-0 |