| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
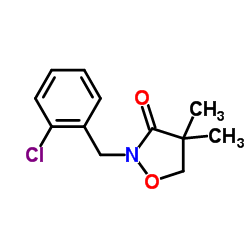 |
异恶草酮
CAS:81777-89-1 |
|
 |
草达灭标准溶液
CAS:2212-67-1 |
|
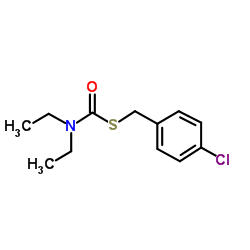 |
禾草丹
CAS:28249-77-6 |