Zn(II)-cyclam based chromogenic sensors for recognition of ATP in aqueous solution under physiological conditions and their application as viable staining agents for microorganism.
Prasenjit Mahato, Amrita Ghosh, Sanjiv K Mishra, Anupama Shrivastav, Sandhya Mishra, Amitava Das
文献索引:Inorg. Chem. 50(9) , 4162-70, (2011)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
Two chromogenic complexes, L.Zn (where L is (E)-4-((4-(1,4,8,11-tetraazacyclotetradecan-1-ylsulfonyl)phenyl)diazenyl)-N,N-dimethylaniline) and its [2]pseudorotaxane form (α-CD.L.Zn), were found to bind preferentially to adenosine triphosphate (ATP), among all other common anions and biologically important phosphate (AMP, ADP, pyrophosphate, and phosphate) ions in aqueous HEPES buffer medium of pH 7.2. Studies with live cell cultures of prokaryotic microbes revealed that binding of these two reagents to intercellular ATP, produced in situ, could be used in delineating the gram-positive and the gram-negative bacteria. More importantly, these dyes were found to be nontoxic to living microbes (eukaryotes and prokaryotes) and could be used for studying the cell growth dynamics. Binding to these two viable staining agents to intercellular ATP was also confirmed by spectroscopic studies on cell growth in the presence of different respiratory inhibitors that influence the intercellular ATP generation.© 2011 American Chemical Society
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
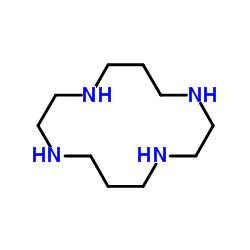 |
1,4,8,11-四氮杂环十四烷
CAS:295-37-4 |
C10H24N4 |
|
Role of ligand to control the mechanism of nitric oxide redu...
2011-12-05 [Inorg. Chem. 50(23) , 11868-76, (2011)] |
|
A reversible nanoswitch as an ON-OFF photocatalyst.
2012-12-14 [Chem. Commun. (Camb.) 48(96) , 11730-2, (2012)] |
|
Liposome encapsulation of a photochemical NO precursor for c...
2012-10-01 [Mol. Pharm. 9(10) , 2950-5, (2012)] |
|
Photochemistry of trans-Cr(cyclam)(ONO)2+, a nitric oxide pr...
2011-05-16 [Inorg. Chem. 50(10) , 4453-62, (2011)] |
|
Model studies of methyl CoM reductase: methane formation via...
2012-05-07 [Inorg. Chem. 51(9) , 5173-87, (2012)] |