| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
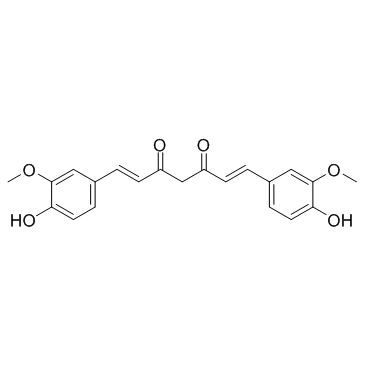 |
姜黄素
CAS:458-37-7 |
|
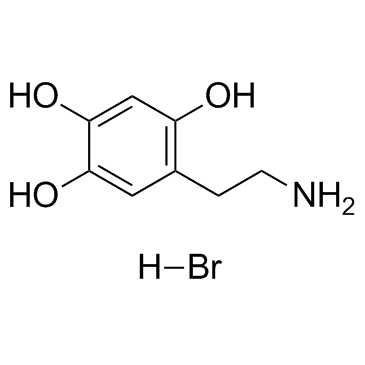 |
6-羟基多巴胺氢溴酸盐
CAS:636-00-0 |
|
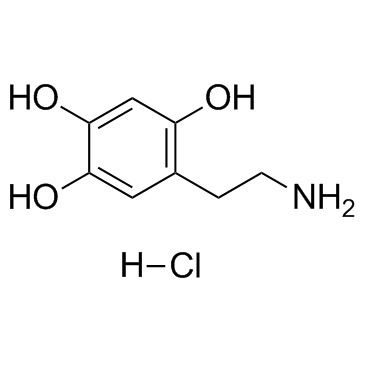 |
6-羟基多巴胺盐酸盐
CAS:28094-15-7 |