| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
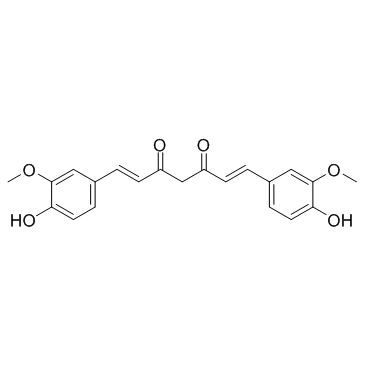 |
姜黄素
CAS:458-37-7 |
|
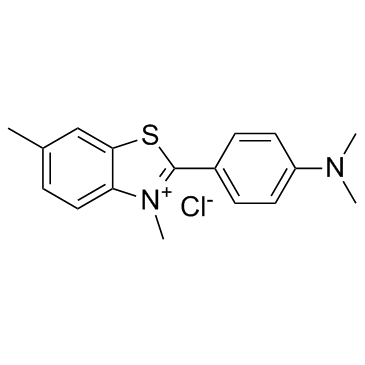 |
硫黄素 T
CAS:2390-54-7 |
|
 |
硫磺素
CAS:1326-12-1 |
|
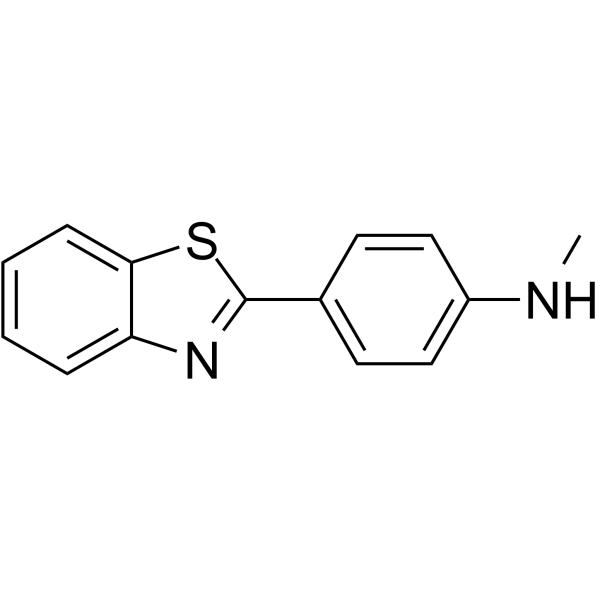 |
2-(4'-甲基氨基苯基)苯并噻唑
CAS:439858-28-3 |