Fluorescence optical detection in situ for real-time monitoring of cytochrome P450 enzymatic activity of liver cells in multiple microfluidic devices.
Jong Hwan Sung, Jong-ryul Choi, Donghyun Kim, Michael L Shuler
文献索引:Biotechnol. Bioeng. 104(3) , 516-25, (2009)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
We describe an in situ fluorescence optical detection system to demonstrate real-time and non-invasive detection of reaction products in a microfluidic device while under perfusion within a standard incubator. The detection system is designed to be compact and robust for operation inside a mammalian cell culture incubator for quantitative detection of fluorescent signal from microfluidic devices. When compared to a standard plate reader, both systems showed similar biphasic response curves with two linear regions. Such a detection system allows real-time measurements in microfluidic devices with cells without perturbing the culture environment. In a proof-of-concept experiment, the cytochrome P450 1A1/1A2 activity of a hepatoma cell line (HepG2/C3A) was monitored by measuring the enzymatic conversion of ethoxyresorufin to resorufin. The hepatoma cell line was embedded in Matrigel(TM) construct and cultured in a microfluidic device with medium perfusion. The response of the cells, in terms of P450 1A1/1A2 activity, was significantly different in a plate well system and the microfluidic device. Uninduced cells showed almost no activity in the plate assay, while uninduced cells in Matrigel(TM) with perfusion in a microfluidic device showed high activity. Cells in the plate assay showed a significant response to induction with 3-Methylcholanthrene while cells in the microfluidic device did not respond to the inducer. These results demonstrate that the system is a potentially useful method to measure cell response in a microfluidic system.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
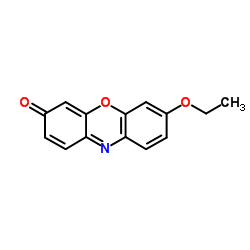 |
乙氧基试卤灵
CAS:5725-91-7 |
C14H11NO3 |
|
The licorice flavonoid isoliquiritigenin reduces DNA-binding...
2014-09-25 [Chem. Biol. Interact. 221 , 70-6, (2014)] |
|
Inhibition of cytochrome P450 1A2-mediated metabolism and pr...
2011-01-01 [Drug Metab. Lett. 5(1) , 6-16, (2011)] |
|
The aryl hydrocarbon receptor pathway and the response to 3-...
2011-01-01 [Drug Metab. Dispos. 39(1) , 83-91, (2011)] |
|
Up-regulation of cytochrome P450 and phase II enzyme systems...
2011-03-01 [Lung Cancer 71(3) , 298-305, (2011)] |
|
CYP1D1, pseudogenized in human, is expressed and encodes a f...
2011-02-01 [Biochem. Pharmacol. 81(3) , 442-50, (2011)] |