| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
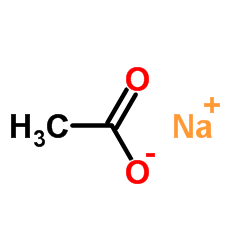 |
乙酸钠
CAS:127-09-3 |
|
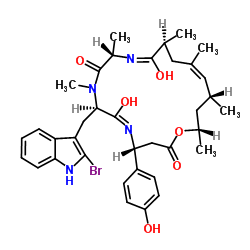 |
Jasplakinolide
CAS:102396-24-7 |
|
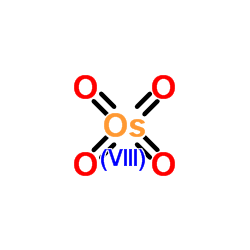 |
锇酸酐
CAS:20816-12-0 |