| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
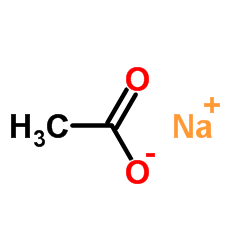 |
乙酸钠
CAS:127-09-3 |
|
 |
十二烷基硫酸钠
CAS:151-21-3 |
|
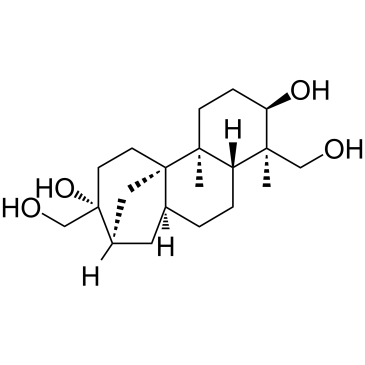 |
阿非科林
CAS:38966-21-1 |
|
![1,1'-[1,4-亚苯基双(亚甲基)]双(1-吡啶鎓)二溴化物 结构式](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/079/14208-10-7.png) |
1,1'-[1,4-亚苯基双(亚甲基)]双(1-吡啶鎓)二溴化物
CAS:14208-10-7 |
|
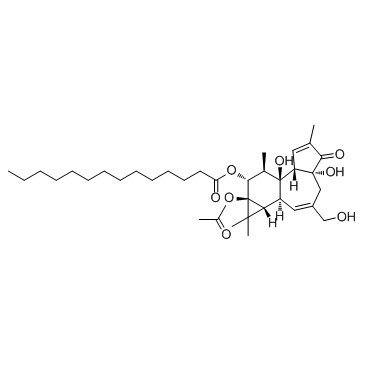 |
12-O-十四烷酰佛波醋酸酯-13
CAS:16561-29-8 |
|
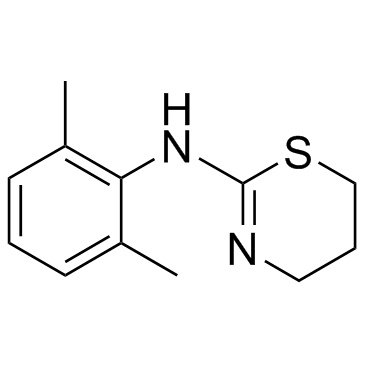 |
赛拉嗪
CAS:7361-61-7 |
|
 |
氯化铵
CAS:12125-02-9 |
|
 |
乙二胺四乙酸
CAS:60-00-4 |
|
 |
4-甲基-7-氧香豆素-β-D-吡喃半乳糖苷
CAS:6160-78-7 |