| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
 |
溴化乙啶
CAS:1239-45-8 |
|
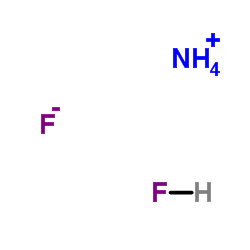 |
氟化氢铵
CAS:1341-49-7 |
|
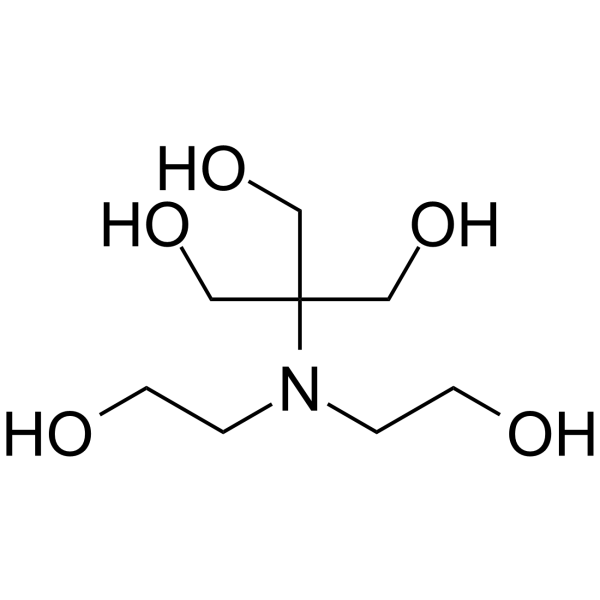 |
二(2-羟乙基)亚氨基三(羟甲基)甲烷
CAS:6976-37-0 |
|
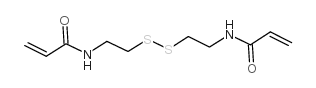 |
N,N'-双(丙稀酰)胱胺
CAS:60984-57-8 |