1,2-Addition of Diethylzinc to a Bis(Imidazolyl)ketone Ligand
Emma Folkertsma, Sanne H. Benthem, Johann T. B. H. Jastrzebski, Martin Lutz, Marc-Etienne Moret, Robertus J. M. Klein Gebbink
文献索引:10.1002/ejic.201701363
全文:HTML全文
摘要
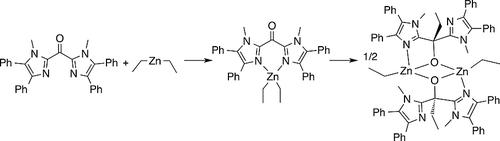
In this study, the selective 1,2-addition of diethylzinc to the ketone functionality of BMdiPhIK [bis(1-methyl-4,5-diphenylimidazolyl)ketone] is shown. The reaction product is isolated in a dimeric form with a planar Zn2(µ-O)2-motif keeping the two monomers together. This compound can serve as a model for reactive intermediates in the catalytic alkylation of ketones with diorganozinc reagents. Hydrolysis of this binuclear zinc compound leads to isolation of the C-alkylated product in 89 % yield. A reaction pathway is proposed in which BMdiPhIK initially coordinates to diethylzinc as a bidentate bis(nitrogen) ligand. This is followed by the homolytic cleavage of the Zn–Et bond and in-cage recombination of the Et-radical and the Zn-coordinated ligand-centered radical, which is mainly localized on the carbonyl moiety of the ligand. Investigations on the selective 1,2 addition of Et2Zn to the ketone BMdiPhIK point at the viability of a radical addition mechanism involving a Zn-coordinated ligand-centered radical.
|
Increased Efficiency of Dye‐Sensitized Solar Cells by Incorp...
2018-04-06 [10.1002/ejic.201800123] |
|
Exploring Synthetic Routes to Heteroleptic UIII, UIV, and Th...
2018-04-06 [10.1002/ejic.201800036] |
|
[Co(MeTAA)] Metalloradical Catalytic Route to Ketenes via Ca...
2018-04-06 [10.1002/ejic.201800101] |
|
Copper(I)–Dioxygen Reactivity in the Isolated Cavity of a Na...
2018-04-06 [10.1002/ejic.201800029] |
|
Insight into Solvent Coordination of an Iron Porphyrin Hydro...
2018-03-25 [10.1002/ejic.201800040] |