Effect of multiscale structural parameters on the mechanical properties of rice stems
Jiale Huang, Wangyu Liu, Feng Zhou, Yujian Peng
文献索引:10.1016/j.jmbbm.2018.03.040
全文:HTML全文
摘要
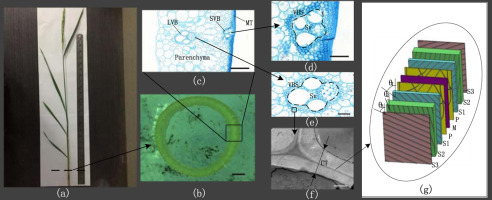
The objective of this study was to investigate the relation between the structural parameters and the mechanical properties of rice stem at different scales. Tensile modulus and bending properties of different kinds of rice stems were measured through tensile and three-point bending tests. The morphology and microstructures of rice stems at different scales are detected by the scanning electron microscope (SEM), transmission electron microscope (TEM) and X-ray diffraction (XRD). It is found that the microfibril angle (MFA) and the volume fraction of the supporting materials dominate the tensile modulus of rice stem. Whereas, the bending properties of rice stem are more sensitive to the structural parameters of the matrix materials. Moreover, compared to the number or volume fraction of small/large vascular bundle, the volume fraction of the mechanical tissue layer in skin exerts a greater influence on the tensile modulus of the rice stem.
|
Acute exposure of white-tailed deer cortical bone to Staphyl...
2018-04-04 [10.1016/j.jmbbm.2018.04.003] |
|
Tribological evaluation of biomedical polycarbonate urethane...
2018-04-03 [10.1016/j.jmbbm.2018.04.001] |
|
Mechanical alterations of the bone-cartilage unit in a rabbi...
2018-04-03 [10.1016/j.jmbbm.2018.03.033] |
|
Swelling of Fiber-Reinforced Soft Tissues is Affected by Fib...
2018-04-03 [10.1016/j.jmbbm.2018.03.039] |
|
Material properties of ultra-high molecular weight polyethyl...
2018-04-03 [10.1016/j.jmbbm.2018.03.029] |