A General Small-Angle X-ray Scattering-Based Screening Protocol Validated for Protein–RNA Interactions
Po-chia Chen, Pawel Masiewicz, Vladimir Rybin, Dmitri Svergun, Janosch Hennig
文献索引:10.1021/acscombsci.8b00007
全文:HTML全文
摘要
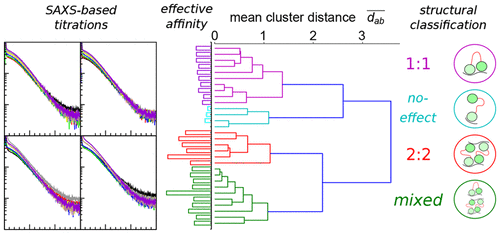
We present a screening protocol utilizing small-angle X-ray scattering (SAXS) to obtain structural information on biomolecular interactions independent of prior knowledge, so as to complement affinity-based screening and provide leads for further exploration. This protocol categorizes ligand titrations by computing pairwise agreement between curves, and separately estimates affinities by quantifying complex formation as a departure from the linear sum properties of solution SAXS. The protocol is validated by sparse sequence search around the native poly uridine RNA motifs of the two-RRM domain Sex-lethal protein (Sxl). The screening of 35 RNA motifs between 4 to 10 nucleotides reveals a strong variation of resulting complexes, revealed to be preference-switching between 1:1 and 2:2 binding stoichiometries upon addition of structural modeling. Validation of select sequences in isothermal calorimetry and NMR titration retrieves domain-specific roles and function of a guanine anchor. These findings reinforce the suitability of SAXS as a complement in lead identification.
|
A Parallel Approach to 7-(Hetero)arylpyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidi...
2018-04-06 [10.1021/acscombsci.8b00032] |
|
Solid-Phase Synthesis of β-Hydroxy Ketones Via DNA-Compatibl...
2018-04-03 [10.1021/acscombsci.8b00001] |
|
Construction of Druglike 2-Amido Benzo[d]imidazole Analogues...
2018-03-26 [10.1021/acscombsci.8b00004] |
|
Development and Application of a Sensitive Peptide Reporter ...
2018-03-23 [10.1021/acscombsci.7b00193] |
|
Aptamer-Based Paper Strip Sensor for Detecting Vibrio fische...
2018-03-22 [10.1021/acscombsci.7b00190] |