Cassava starch-sodium allylsulfonate-acryl amide graft copolymer as an effective inhibitor of aluminum corrosion in HCl solution
Xianghong Li, Shuduan Deng, Tong Lin, Xiaoguang Xie, Guanben Du
文献索引:10.1016/j.jtice.2018.03.002
全文:HTML全文
摘要
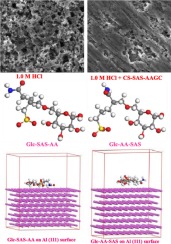
Cassava starch-sodium allylsulfonate-acryl amide graft copolymer (CS-SAS-AAGC) was prepared by in situ polymerization of sodium allylsulfonate (SAS) and acryl amide (AA) in the presence of cassava starch (CS). The inhibition performance was tested by immersing aluminum in HCl solution using weight loss and electrochemical methods. CS-SAS-AAGC showed an inhibition efficiency as high as 95% at low inhibitor concentration of 100 mg/L. The inhibitive performance is much higher than that of CS, SAS, AA, CS/AA, CS/SAS or CS/AA/SAS mixture. The adsorption of CS-SAS-AAGC on aluminum surface was found to obey Langmuir adsorption isotherm. CS-SAS-AAGC behaves as a mixing-type inhibitor, while mainly inhibiting the cathodic reaction. Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) has two time constants with a large capacitive loop at high frequencies followed by also a large inductive one at low frequencies. The inhibition of aluminum surface by CS-SAS-AAGC is evidenced through scanning electron microscope (SEM) and contact angle images. The adsorption mechanism was theoretically analyzed by quantum chemical calculation and molecular dynamic (MD) simulation.
|
Extremely high photocatalytic H2 evolution of novel Co3O4/Cd...
2018-04-04 [10.1016/j.jtice.2018.03.035] |
|
Kinetics of hydrogen generation on NaBH4 powders using cobal...
2018-04-01 [10.1016/j.jtice.2018.03.022] |
|
Synthesis of mechanically robust epoxy cross-linked silica a...
2018-04-01 [10.1016/j.jtice.2018.03.019] |
|
Scrap iron packed in a Ti mesh cage as a sacrificial anode f...
2018-03-31 [10.1016/j.jtice.2018.03.016] |
|
Synthesis of glycerol carbonate from glycerol and diethyl ca...
2018-03-31 [10.1016/j.jtice.2018.03.023] |