Impact of heat-light soaking on potassium fluoride treated CIGS solar cells with CdS buffer layer
Ishwor Khatri, Kosuke Shudo, Junpei Matsuura, Mutsumi Sugiyama, Tokio Nakada
文献索引:10.1002/pip.2962
全文:HTML全文
摘要
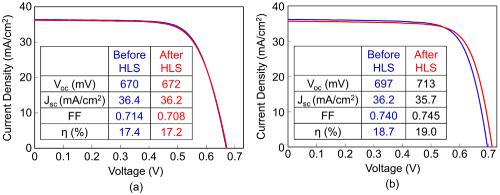
In this study, the effects of light-soaking (LS), heat-soaking (HS), and combined LS and HS, that is, heat-light soaking (HLS) on potassium fluoride (KF)-treated and KF-free copper indium gallium selenide (CIGS) solar cells with CBD-CdS buffer layer were investigated. LS and HS did not change the basic solar cell parameters of CIGS solar cells when they were performed separately. In contrast, HLS improved cell efficiency with increased open-circuit-voltage for KF-treated CIGS solar cells, whereas it reduced cell performance for KF-free CIGS cells. Capacitance-voltage measurements confirmed a significantly increased carrier concentration in KF-treated CIGS solar cells, as compared to KF-free cells by HLS. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy measurement revealed that the HLS did not change the atomic concentration of Cd, S, and O in CBD-CdS buffer layer. However, the concentration of Na atoms slightly increased at the CIGS surface region, as confirmed from SIMS measurement. It implies a possible reason for increased carrier concentration in KF-treated CIGS solar cells after HLS. Temperature-dependent current-voltage measurements suggests that HLS modify a K-containing new layer and affects cell performance. Current-voltage curves for KF-free (a) and KF-treated (b) CIGS solar cells with CdS buffer layer before (blue lines) and after (red lines) heat-light soaking (HLS). The open circuit voltage, fill factor and cell efficiency improved only for KF-treated CIGS solar cells after HLS post-treatment. The reason for this behavior is due to K-containing new layer at near-surface region. The combined alkali metal- and HLS-post-treatments have a potential of further improvement in efficiencies of CIGS solar cells.
|
Regional photovoltaic power fluctuations within frequency re...
2018-03-06 [10.1002/pip.2999] |
|
Investigating PID shunting in polycrystalline silicon module...
2018-02-27 [10.1002/pip.2996] |
|
Comparing supply and demand models for future photovoltaic p...
2018-02-22 [10.1002/pip.2997] |
|
Optical properties and performance of pyramidal texture sili...
2018-02-09 [10.1002/pip.2994] |
|
Improving performance by Na doping of a buffer layer—chemica...
2018-02-09 [10.1002/pip.2993] |