Modeling Psychomotor Retardation using iPSCs from MCT8-Deficient Patients Indicates a Prominent Role for the Blood-Brain Barrier
Gad D. Vatine, Abraham Al-Ahmad, Bianca K. Barriga, Soshana Svendsen, Ariel Salim, Leslie Garcia, Veronica J. Garcia, Ritchie Ho, Nur Yucer, Tongcheng Qian, Ryan G. Lim, Jie Wu, Leslie M. Thompson, Weston R. Spivia, Zhaohui Chen, Jennifer Van Eyk, Sean P. Palecek, Samuel Refetoff, Eric V. Shusta, Clive N. Svendsen
文献索引:10.1016/j.stem.2017.04.002
全文:HTML全文
摘要
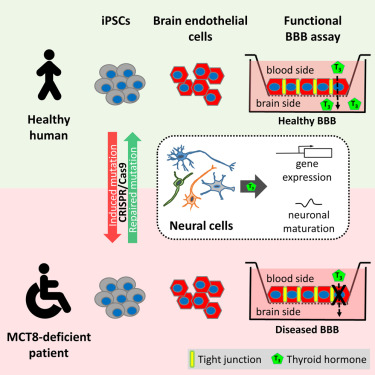
Inactivating mutations in the thyroid hormone (TH) transporterMonocarboxylate transporter 8(MCT8) cause severe psychomotor retardation in children. Animal models do not reflect the biology of the human disease. Using patient-specific induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs), we generated MCT8-deficient neural cells that showed normal TH-dependent neuronal properties and maturation. However, the blood-brain barrier (BBB) controls TH entry into the brain, and reduced TH availability to neural cells could instead underlie the diseased phenotype. To test potential BBB involvement, we generated an iPSC-based BBB model of MCT8 deficiency, and we found that MCT8 was necessary for polarized influx of the active form of TH across the BBB. We also found that a candidate drug did not appreciably cross the mutant BBB. Our results therefore clarify the underlying physiological basis of this disorder, and they suggest that circumventing the diseased BBB to deliver active TH to the brain could be a viable therapeutic strategy.
|
ASCL1 Reorganizes Chromatin to Direct Neuronal Fate and Supp...
2017-07-13 [10.1016/j.stem.2017.06.004] |
|
Lineage Tracing: Papers and Progress
2017-07-06 [10.1016/j.stem.2017.06.015] |
|
Intestinal Enteroendocrine Lineage Cells Possess Homeostatic...
2017-07-06 [10.1016/j.stem.2017.06.014] |
|
Direct Neuronal Reprogramming: Achievements, Hurdles, and Ne...
2017-07-06 [10.1016/j.stem.2017.06.011] |
|
Making HSCs on Demand: Looking Ahead
2017-07-06 [10.1016/j.stem.2017.06.010] |