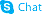5579-84-0
| Name | Betahistine dihydrochloride |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
MFCD00012813
N-Methyl-2-(2-pyridinyl)ethanamine dihydrochloride N-methyl-2-(pyridin-2-yl)ethanamine dihydrochloride 2-Pyridineethanamine, N-methyl-, hydrochloride (1:2) Betahistine Hydrochloride N-Methyl-2-pyridineethanamine Dihydrochloride N-methyl-2-pyridin-2-ylethanamine,dihydrochloride EINECS 226-966-5 Betahistine (dihydrochloride) |
| Description | Betahistine Dihydrochloride is a histamine H3 receptors inhibitor used as an antivertigo drug.Target: Histamine ReceptorBetahistine, a structural analogue of histamine with weak histamine H(1) receptor agonist and more potent H(3) receptor antagonist properties. Betahistine acts centrally by enhancing histamine synthesis within tuberomammillary nuclei of the posterior hypothalamus and histamine release within vestibular nuclei through antagonism of H(3) autoreceptors [1].Therapeutic effects of betahistine in vestibular disorders result from its antagonist properties at histamine H(3) receptors (H(3)Rs). On inhibition of cAMP formation and [(3)H]arachidonic acid release, betahistine behaved as a nanomolar inverse agonist and a micromolar agonist. After acute oral administration, Betahistine increased t-MeHA levels with an ED(50) of 2 mg/kg, a rightward shift probably caused by almost complete first-pass metabolism. Therapeutic effects of betahistine result from an enhancement of histamine neuron activity induced by inverse agonism at H(3) autoreceptors [2]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| References |
| Density | 0.967 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 210.9ºC at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 150-154 °C |
| Molecular Formula | C8H14Cl2N2 |
| Molecular Weight | 209.116 |
| Flash Point | 96.7ºC |
| Exact Mass | 208.053406 |
| PSA | 24.92000 |
| LogP | 2.83840 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Gloves;type N95 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter |
|---|---|
| Hazard Codes | Xi |
| Safety Phrases | S24/25 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | UT2969000 |
| HS Code | 2933399090 |
| HS Code | 2933399090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2933399090. other compounds containing an unfused pyridine ring (whether or not hydrogenated) in the structure. VAT:17.0%. Tax rebate rate:13.0%. . MFN tariff:6.5%. General tariff:20.0% |