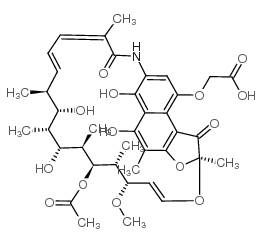
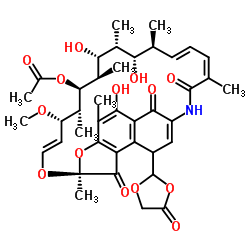
13553-79-2
| Name | Rifamycin S |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Rifamycin,1,4-dideoxy-1,4-dihydro-1,4-dioxo
UNII-PI53N820JV rifomycin-S rifamycin-S (7S,9E,11S,12R,13S,14R,15R,16R,17S,18S,19E,21Z)-2,15,17-Trihydroxy-11-methoxy-3,7,12,14,16,18,22-heptamethyl-6,23,27,29-tetraoxo-8,30-dioxa-24-azatetracyclo[23.3.1.1.0]triaconta-1(28),2,4,9,19,21,25-heptaen-13-yl acetate NCI 144-130 (2S,12Z,14E,16S,17S,18R,19R,20R,21S,22R,23S,24E)-5,17,19-trihydroxy-23-methoxy-2,4,12,16,18,20,22-heptamethyl-1,6,9,11-tetraoxo-1,2,6,9-tetrahydro-2,7-(epoxypentadeca[1,11,13]trienoimino)naphtho[2,1-b]furan-21-yl acetate EINECS 236-938-4 2,7-(Epoxy[1,11,13]pentadecatrienoimino)naphtho[2,1-b]furan-1,6,9,11(2H)-tetrone, 21-(acetyloxy)-5,17,19-trihydroxy-23-methoxy-2,4,12,16,18,20,22-heptamethyl-, (2S,12Z,14E,16S,17S,18R,19R,20R,21S,22R,23S,24E)- (12S,3E,5S,13E,15Z)-7t-acetoxy-15,9c,11t-trihydroxy-5r-methoxy-12,4,6t,8c,10c,12t,16-heptamethyl-2-oxa-18-aza-1(2,7)-naphtho[2,1-b]furana-cyclooctadecaphane-3,13,15-triene-11,6,9,17-tetraone rifaximin S O1,O4-didehydro-rifamycin (7S,9E,11S,12R,13S,14R,15R,16R,17S,18S,19E,21Z)-2,15,17-Trihydroxy-11-methoxy-3,7,12,14,16,18,22-heptamethyl-6,23,27,29-tetraoxo-8,30-dioxa-24-azatetracyclo[23.3.1.1.0]triaconta-1(28),2,4,9 ,19,21,25-heptaen-13-yl acetate 1,4-Dideoxy-1,4-dihydro-1,4-dioxorifamycin RifamycinS |
| Description | Rifamycin S is a quinone and an antibiotic agnet against Gram-positive bacteria (including MRSA). Rifamycin S is the oxidized forms of a reversible oxidation-reduction system involving two electrons. Rifamycin S generates reactive oxygen species (ROS) and inhibits microsomal lipid peroxidation. Rifamycin S can be used for tuberculosis and leprosy[1][2][3]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Gram-positive bacteria[3] Reactive oxygen species (ROS)[1] |
| In Vitro | The inhibition of bacterial growth by Rifamycin SV is due to the production of active species of oxygen resulting from the oxidation-reduction cycle of Rifamycin SV in the cells. The aerobic oxidation of Rifamycin SV to Rifamycin S is induced by metal ions, such as Mn2+, Cu2+, and Co2+. The most effective metal ion is Mn2+[2]. |
| In Vivo | Rat liver sub-mitochondrial particles also generated hydroxyl radical in the presence of NADH and Rifamycin S. NADH dehydrogenase (complex I) as the major component involved in the reduction of Rifamycin S. Compared to NADPH, NADH is almost as effective (Rifamycin S) in catalyzing the interactions of these antibiotics with rat liver microsomes. Rifamycin S is shown to be readily reduced to Rifamycin SV, the corresponding hydroquinone by Fe(II). Rifamycin S forms a detectable Fe(II)-(Rifamycin S)3 complex. The Fe:ATP induced lipid peroxidation is completely inhibited by Rifamycin S. Rifamycin S can interact with rat liver microsomes to undergo redox-cycling, with the subsequent production of hydroxyl radicals when iron complexes are present[1]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 917.4±65.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 179-181ºC (dec.) |
| Molecular Formula | C37H45NO12 |
| Molecular Weight | 695.753 |
| Flash Point | 508.6±34.3 °C |
| Exact Mass | 695.294189 |
| PSA | 194.99000 |
| LogP | 2.87 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±0.3 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.605 |
| Storage condition | 2-8°C |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| RTECS | KD1925000 |
|---|---|
| HS Code | 2941903000 |
|
~92% 
13553-79-2 |
| Literature: Seong, Baik Lin; Han, Moon Hi Chemistry Letters, 1982 , p. 627 - 628 |
|
~% 
13553-79-2 |
| Literature: Journal of the Chemical Society, Chemical Communications, , p. 395 - 396 |
|
~% 
13553-79-2 |
| Literature: Journal of the Chemical Society, Chemical Communications, , p. 395 - 396 |
| Precursor 3 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 2 | |
| HS Code | 2941903000 |
|---|