115550-35-1
| Name | Marbofloxacin |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Marbofloxacino [INN-Spanish]
Marbofloxacin (INN) Marbocyl 9-Fluoro-3-methyl-10-(4-methyl-1-piperazinyl)-7-oxo-2,3-dihydro-7H-[1,3,4]oxadiazino[6,5,4-ij]quinoline-6-carboxylic acid Marbofloxacin 9-Fluoro-2,3-dihydro-3-methyl-10-(4-methyl-1-piperazinyl)-7-oxo-7H-pyrido[3,2,1-ij][4,1,2]benzoxadiazine-6-carboxylic Acid MFCD00864820 9-Fluoro-3-methyl-10-(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)-7-oxo-2,3-dihydro-7H-[1,3,4]oxadiazino[6,5,4-ij]quinoline-6-carboxylic acid 7H-1,3,4-Oxadiazino[6,5,4-ij]quinoline-6-carboxylic acid, 9-fluoro-2,3-dihydro-3-methyl-10-(4-methyl-1-piperazinyl)-7-oxo- UNII-8X09WU898T Zeniquin 2,3-Dihydro-9-fluoro-3-methyl-10-(4-methyl-1-piperazinyl)-7-oxo-7H-pyrido[3,2,1-ij][4,1,2]benzoxadiazine-6-carboxylic Acid |
| Description | Marbofloxacin is a potent antibiotic of which depends upon its inhibition of DNA-gyrase. Marbofloxacin is a synthetic, broad spectrum bactericidal agent.Target: DNA-gyraseMarbofloxacin is a third-generation fluoroquinolone for veterinary use, the antimicrobial of which depends upon its inhibition of DNA-gyrase and topoisomerase IV. With a broad spectrum bactericidal activity and good efficacy, marbofloxacin is indicated for dermatological, respiratory and urinary tract infections due to both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria and Mycoplasma [1].Administration of Marbofloxacin at 6 mg/kg once daily for 7 days in a Staphylococcus aureus infection in tissue cages in ponies is not effective for the elimination of S. aureus infections from secluded sites [2]. The pharmacokinetic properties of marbofloxacin were investigated in 6 horses after i.v., subcutaneous and oral administration of a single dose of 2 mg/kg bwt and the minimal inhibitory concentrations (MIC) assessed for bacteria isolated from equine infectious pathologies. The clearance of marbofloxacin was mean +/- s.d. 0.25 +/- 0.05 l/kg/h and the terminal half-life 756 +/- 1.99 h. The marbofloxacin absolute bioavailabilities after subcutaneous and oral administration were 98 +/- 11% and 62 +/- 8%, respectively. Considering the breakpoint values of efficacy indices for fluoroquinolones, a marbofloxacin dosage regimen of 2 mg/kg bwt/24 h by i.v., subcutaneous or oral routes was more appropriate for enterobacteriaceae than for S. aureus [3]. Toxicity: cramps; vomiting; anorexia; soft stools; diarrhoea |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| References |
[1]. Shen J, et al. Marbofloxacin. Acta Crystallogr Sect E Struct Rep Online. 2012 Apr 1;68(Pt 4):o998-9. |
| Density | 1.6±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 570.5±60.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 268-269ºC |
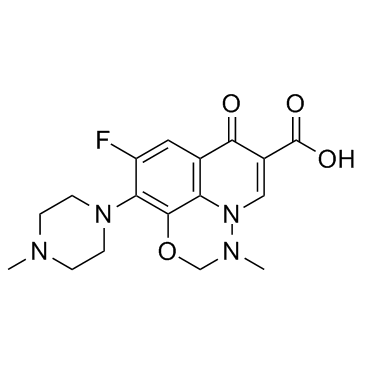
| Molecular Formula | C17H19FN4O4 |
| Molecular Weight | 362.356 |
| Flash Point | 298.8±32.9 °C |
| Exact Mass | 362.139038 |
| PSA | 78.25000 |
| LogP | -0.55 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.7 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.701 |
| Storage condition | -20°C Freezer, Under Inert Atmosphere |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Gloves |
|---|---|
| Hazard Codes | Xi: Irritant; |
| Risk Phrases | R52/53 |
| Safety Phrases | S61 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| RTECS | UU8815140 |
| HS Code | 2934999090 |
| HS Code | 2934999090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2934999090. other heterocyclic compounds. VAT:17.0%. Tax rebate rate:13.0%. . MFN tariff:6.5%. General tariff:20.0% |