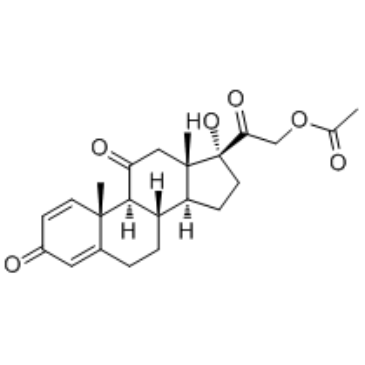
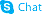50-04-4
| Name | Cortisone acetate |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
MFCD00003609
17α,21-Dihydroxy-4-pregnene-3,11,20-trione 21-acetate Pregn-4-ene-3,11,20-trione, 21- (acetyloxy)-17-hydroxy- 2-[(8S,9S,10R,13S,14S,17R)-17-hydroxy-10,13-dimethyl-3,11-dioxo-2,3,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17-tetradecahydro-1H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-17-yl]-2-oxoethyl acetate 21-Acetoxy-4-pregnen-17α-ol-3,11,20-trione 4-Pregnene-17α,21-diol-3,11,20-trione 21-acetate Cortisone, 21-acetate [2-[(8S,9S,10R,13S,14S,17R)-17-hydroxy-10,13-dimethyl-3,11-dioxo-1,2,6,7,8,9,12,14,15,16-decahydrocyclopenta[a]phenanthren-17-yl]-2-oxoethyl] acetate acétate de 2-[(8S,9S,10R,13S,14S,17R)-17-hydroxy-10,13-diméthyl-3,11-dioxo-2,3,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17-tétradécahydro-1H-cyclopenta[a]phénanthrén-17-yl]-2-oxoéthyle EINECS 200-006-5 17-Hydroxy-3,11,20-trioxopregn-4-en-21-yl acetate 2-[(8S,9S,10R,13S,14S,17R)-17-Hydroxy-10,13-dimethyl-3,11-dioxo-2,3,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17-tetradecahydro-1H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-17-yl]-2-oxoethylacetat Cortisone Acetate 4-Pregnene-3,11,20-trione, 17α,21-dihydroxy-, 21-acetate Pregn-4-ene-3,11,20-trione, 21-(acetyloxy)-17-hydroxy- Cortisone (acetate) |
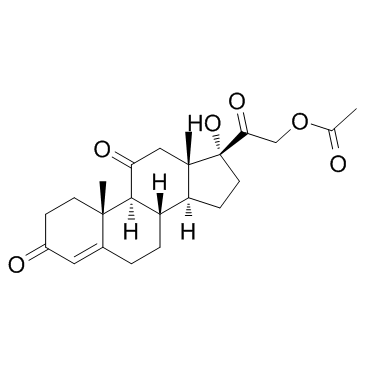
| Description | Cortisone acetate (17-hydroxy-11-dehydrocorticosterone), a 21-carbon steroid hormone, is one of the main hormones released by the adrenal gland in response to stress.IC50 Value: Target: Glucocorticoid Receptorin vitro: Cortisone suppressed this apoptosis at a concentration range of 1-10,000 ng/ml (2.8-28,000 nM) dose-dependently. Suppression of cortisol-induced apoptosis by cortisonewas consistently observed in PBMCs derived from 16 healthy subjects. Examination for inhibitory activities of the steroids against [3H]dexamethasone binding to PBMCs suggested that cortisone can bind cellular GC-receptors (GC-Rs), but the affinity of cortisone to GCRs is 1/30 or less than that of cortisol [1]. Apoptosis was also readily induced in primary cultures of third trimester decidual cells when treated with cortisol, cortisone, or dexamethasone (all 100 nM for 24 h) [2]. in vivo: The effects of a single dose of cortisone acetate (5 or 10 mg/100 g body weight) on B cells were examined in young chickens. A dose-dependent increase in numbers of circulating B lymphocytes and a change in their Ig-class distribution were followed by parallel increase in splenic plasma cells and serum immunoglobulins. The higher dose of cortisone produced changes in Bmu and Bgamma cells, whereas the lower dose primarily affected Bmu cells [3]. Adult female CD-1 mice received daily injections of cortisone acetate (0--50 mg/kg subcutaneously) and/or amphotericin B (0--12.5 mg/kg intraperitoneally) in a checkerboard combination dosage pattern for 30 days. Dosages of amphotericin B and cortisone acetate that produced little or no mortality individually produced significant (P less than 0.005) mortality in combination [4].Toxicity: Oral use of cortisone has a number of potential systemic side-effects: hyperglycemia, insulin resistance, diabetes mellitus, osteoporosis, anxiety, depression, amenorrhoea, cataracts and glaucoma, among other problems. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| References |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 577.3±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 237-240 °C(lit.) |
| Molecular Formula | C23H30O6 |
| Molecular Weight | 402.481 |
| Flash Point | 197.3±23.6 °C |
| Exact Mass | 402.204254 |
| PSA | 97.74000 |
| LogP | 2.53 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±3.6 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.566 |
| Stability | Stable. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
MUTATION DATA
|
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Gloves;type N95 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter |
|---|---|
| Risk Phrases | R22;R36/37 |
| Safety Phrases | S22-S36/37 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | GM9140000 |
|
~% 
50-04-4 |
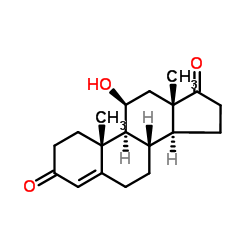
| Literature: Kritchevsky et al. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 1952 , vol. 74, p. 483,485 |
|
~% 
50-04-4 |
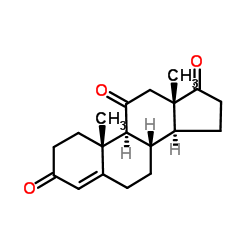
| Literature: Poos et al. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 1954 , vol. 76, p. 5031,5033 |
|
~% 
50-04-4 |
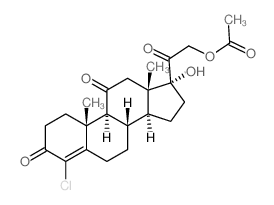
| Literature: Mason; Sprague Journal of Biological Chemistry, 1948 , vol. 175, p. 451,455 Full Text Show Details Reichstein Helvetica Chimica Acta, 1937 , vol. 20, p. 978,987 |
|
~% 
50-04-4 |
| Literature: Mason; Sprague Journal of Biological Chemistry, 1948 , vol. 175, p. 451,455 Full Text Show Details Reichstein Helvetica Chimica Acta, 1937 , vol. 20, p. 978,987 |
|
~% 
50-04-4 |
| Literature: Mason; Sprague Journal of Biological Chemistry, 1948 , vol. 175, p. 451,455 Full Text Show Details Reichstein Helvetica Chimica Acta, 1937 , vol. 20, p. 978,987 |
|
~% 
50-04-4 |
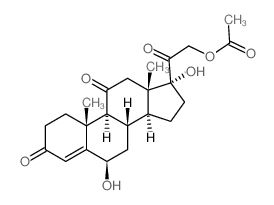
| Literature: Kane; Tsuji Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 1983 , vol. 72, # 1 p. 30 - 35 |
|
~% 
50-04-4 |
| Literature: Sarett Journal of Biological Chemistry, 1946 , vol. 162, p. 601,6307 |
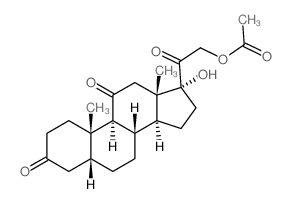
| Precursor 5 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 8 | |