E-64d
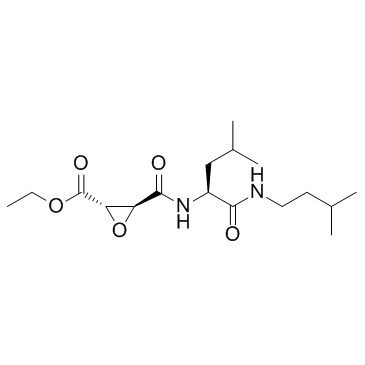
E-64d structure
|
Common Name | E-64d | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 88321-09-9 | Molecular Weight | 342.431 | |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 470.5±55.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C17H30N2O5 | Melting Point | 126.2°C | |
| MSDS | USA | Flash Point | 238.4±31.5 °C | |
Use of E-64dAloxistatin (E64d) is a cell-permeable and irreversible broad-spectrum cysteine protease inhibitor. |
| Name | est |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Aloxistatin (E64d) is a cell-permeable and irreversible broad-spectrum cysteine protease inhibitor. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Cysteine protease[1] |
| In Vitro | Inhibition of protease-resistant prion protein (PrP-res) accumulation in ScNB cells by cysteine protease inhibitor Aloxistatin (E64d) with IC50 of 0.5±0.11 μM. For the cell surface PrP-sen detection, PrP-sen is immunoprecipitated from media treated with phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C (PIPLC) to release pulse-35S-labeled PrP-sen from the cell surface. Aloxistatin is maintained at 15 μM, respectively, in the labeling media of all but the control cells [1]. Aloxistatin (E64d) (which specifically blocks cysteine proteases, but not serine proteases such as granzymes) is able to completely block turnover of the CatL substrate Z-Phe-Arg-aminomethylcoumarin, when pre-incubated with NK-92 or YT 5 cells[2]. Aloxistatin (E64d) is a broad-spectrum cell-permeable inhibitor of cysteine proteases[3]. |
| In Vivo | Oral administration of Aloxistatin (E64d) to guinea pigs results in a dose-dependent reduction in brain, CSF and plasma Aβ(40) and Aβ(42). Aloxistatin also causes a biphasic dose-dependent reduction in brain CTFβ. Aloxistatin causes a dose-dependent increase in brain sAβPPα. The mean sAβPPα levels are significantly higher than the no dose group for Aloxistatin doses of 5 mg/kg/day or greater with the highest Aloxistatin dose resulting in the maximum increase in sAβPPα of about 54% more than the control group. Similar to the Aβ effect, oral Aloxistatin administration produces a biphasic dose-dependent reduction in brain cathepsin B activity. The minimum effective dose is about 1 mg/kg/day with the highest Aloxistatin dose causing the maximum reduction in brain cathepsin B activity of about 91% lower than that of the control group. Thus, Aloxistatin reduces guinea pig brain cathepsin B activity in a manner which is consistent with the compound inhibiting cathepsin B β-secretase activity[4]. Aloxistatin (E64d) inhibits the increases in the expression of AT1AR and ACE genes in rats. Administration of Olmesartan or Aloxistatin reduces the increase in the superoxide production of the intramyocardial coronary arteries in HF rats[5]. |
| Kinase Assay | The CTLs and NK cells (0.8×106/mL) are treated with the inhibitors L1 (10-20 μM) or Aloxistatin (20-30 μM) for 24 hr at 37°C in 24-well plates. Cells are then used in 51Cr-release assays or are lysed to examine perforin in Western blots. The inhibitor is also added at the same concentration during the 4 hr reactions in some 51Cr-release assays, as indicated. Cell lysates are prepared using NP-40 lysis buffer (25 mM HEPES, 250 mM NaCl, 2.5 mM ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid, 0.1% volume/volume Nonidet P-40) and total protein concentration is determined using the Bradford assay. Equal amounts of protein are loaded and resolved on 8% SDS-PAGE gels. Human or mouse perforin is detected using the appropriate antibodies as indicated. Anti-actin antibody is used as a loading control[2]. |
| Cell Assay | Cell proliferation and apoptosis are assessed by staining for a proliferation marker, Ki67, or an apoptotic marker, cleaved caspase 3, following the protocol described above for the polarity markers. MCF10 variants are grown in 3D rBM overlay cultures for 4 days and are treated with 0.1 % DMSO, 5 μM CA074Me or 5 μM Aloxistatin. The percentage of structures that are positive for Ki67 or cleaved caspase 3 is determined by counting a total of 100 structures on two separate coverslips with a Zeiss Axiophot epifluorescent microscope. Structures are considered Ki67 positive if they contained at least one cell staining for Ki67. Structures are considered to be caspase 3 positive if they contained at least one cell that is positive for cleaved caspase 3 and the positive cell(s) is not localized in the center of a developing lumen[3]. |
| Animal Admin | Mice and Pigs[4] Guinea Pigs (male, Hartley strain, average weight 400 g corresponding to animals about 6 weeks old) are used. Male transgenic mice expressing human AβPP containing the wt β-secretase site and the London mutant β-secretase site sequences are used. Delivering a drug by gavage offers the advantage of accurate dosing but is traumatic and thus only suitable for relatively short dosing periods (up to about a week). Delivery by gavage is used for the guinea pig studies. Aloxistatin is suspended in Me2SO at the indicated concentrations (0.1, 1.0, 5, and 10 mg/kg) and administered by gavage daily using a feeding tube. Vehicle control animals are treated by gavage of Me2SO alone. Rats[5] Male inbred DS rats are used. Weaned rats are fed laboratory chow containing 0.3% NaCl until 7 weeks of age. DS rats fed an 8% NaCl diet after 7 weeks manifest compensated concentric left ventricular (LV) hypertrophy secondary to hypertension at 12 weeks and a distinct stage of fatal LV failure with lung congestion at 19 weeks. DS rats are therefore fed an 8% NaCl diet from 7 weeks of age and are randomized to an HF group, an Aloxistatin group (10 mg per kg of body mass per day, administered intraperitoneally every other day), or an olmesartan group (3 mg/kg per day in chow) from 12 to 19 weeks of age (n=10 for each group). The doses of olmesartan (an ARB) and Aloxistatin are determined in preliminary experiments and previous studies. DS rats maintained on the 0.3% NaCl diet served as age-matched controls (control group, n=10). At 19 weeks of age, all of the rats are euthanized by an intraperitoneal overdose of sodium pentobarbital (50 mg/kg), and the hearts are removed for biological and histological analyses. Arterial blood is collected from the abdominal aorta for the measurement of renin activity. Systolic blood pressure and heart rate are measured in conscious rats from 7 weeks of age, every week, using a noninvasive tail-cuff method. In separate experiments, 12-week-old DS rats, fed a low-salt diet from 7 weeks of age, are given vehicle, olmesartan, or Aloxistatin in the same manner as in the above experiments (n=5 for each group), and the LV tissues for measuring targeting mRNAs and protein levels are immediately placed in liquid nitrogen and stored at -80°C. |
| References |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 470.5±55.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 126.2°C |
| Molecular Formula | C17H30N2O5 |
| Molecular Weight | 342.431 |
| Flash Point | 238.4±31.5 °C |
| Exact Mass | 342.215485 |
| PSA | 97.03000 |
| LogP | 3.64 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±2.6 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.530 |
| Storage condition | −20°C |
| Water Solubility | Soluble in DMSO, DMF or ethanol |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
MUTATION DATA
|
| Personal Protective Equipment | dust mask type N95 (US);Eyeshields;Gloves |
|---|---|
| Hazard Codes | Xi: Irritant; |
| Risk Phrases | R36/37/38 |
| Safety Phrases | S26;S36 |
| RIDADR | 3077 |
| WGK Germany | 2 |
| RTECS | RR0404300 |
|
Itraconazole suppresses the growth of glioblastoma through induction of autophagy: involvement of abnormal cholesterol trafficking.
Autophagy 10(7) , 1241-55, (2014) Glioblastoma is one of the most aggressive human cancers with poor prognosis, and therefore a critical need exists for novel therapeutic strategies for management of glioblastoma patients. Itraconazol... |
|
|
Polymorphisms in Ion Transport Genes Are Associated with Eggshell Mechanical Property.
PLoS ONE 10 , e0130160, (2015) Eggshell mechanical property traits such as eggshell breaking strength (ESS), eggshell thickness (EST) and eggshell weight (ESW) are most common and important indexes to evaluate eggshell quality in p... |
|
|
Preferential expression of a bromoperoxidase in sporophytes of a red alga, Pyropia yezoensis.
Mar. Biotechnol. 17(2) , 199-210, (2015) A 2,158 bp cDNA (PyBPO1) encoding a bromoperoxidase (BPO) of 625 amino acids was isolated from Pyropia yezoensis. Phylogenetic analysis using amino acid sequences of BPOs suggested that P. yezoensis a... |
| Ethyl (2S,3S)-3-({(2S)-4-methyl-1-[(3-methylbutyl)amino]-1-oxo-2-pentanyl}carbamoyl)-2-oxiranecarboxylate |
| L-trans-epoxysuccinyl-Leu-3-methylbutylamide-ethyl ester |
| ep453 |
| 2-Oxiranecarboxylic acid, 3-[(Z)-hydroxy[[(1S)-1-[(Z)-hydroxy[(3-methylbutyl)imino]methyl]-3-methylbutyl]imino]methyl]-, ethyl ester, (2S,3S)- |
| LOXASTATIN |
| Ethyl (2S,3S)-3-({(2S)-4-methyl-1-[(3-methylbutyl)amino]-1-oxopentan-2-yl}carbamoyl)oxirane-2-carboxylate |
| aloxistatin |
| 2-Oxiranecarboxylic acid, 3-[[[(1S)-3-methyl-1-[[(3-methylbutyl)amino]carbonyl]butyl]amino]carbonyl]-, ethyl ester, (2S,3S)- |
| LOXISTATIN |
| (2S-(2a,3b(R*)))-3-(((3-Methyl-1-(((3-methylbutyl)amino)carbonyl)butyl)amino)carbonyl)oxiranecarboxylic Acid Ethyl Ester |
| MFCD00132883 |
| (2S,3S)-3-(Ethoxycarbonyl)-N-{(1Z,2S)-1-hydroxy-4-methyl-1-[(3-methylbutyl)imino]-2-pentanyl}-2-oxiranecarboximidic acid |
| E-64D |