Vinflunine Tartrate
Modify Date: 2024-01-06 19:27:23
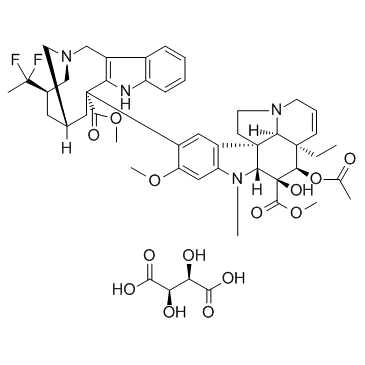
Vinflunine Tartrate structure
|
Common Name | Vinflunine Tartrate | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 1201898-17-0 | Molecular Weight | 967.01600 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C49H60F2N4O14 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | N/A | |
Use of Vinflunine TartrateVinflunine Tartrat is a new vinca alkaloid uniquely fluorinated with the properties of mitotic-arresting and tubulin-interacting activity.Target: Microtubule/TubulinThe major effects of Vinflunine on dynamic instability are a slowing of the microtubule growth rate, an increase in growth duration, and a reduction in shortening duration. The effects of Vinflunine on the readmilling rate is examined by following [3H]GTP incorporation into MAP-rich microtubules, and the IC50 is 0.42 μM [1]. Vinflunine induced mitotic accumulation with IC50 with 18.8 nM, which decreases the centromere dynamicity by 44% and increases the time centromeres spent ina paused state by 63% [2]. Treatment of Vinflunine induces a rapid change in endothelial cell shape: cells retracts and assumes a rounded morphology. Mean IC50 values are 9.9 × 10-5 M × 10-5 M for fibronectin and 5.0× 10-5 M × 10-5 M for type IV collagen. A short 4 hours exposure of endothelial cells to Vinflunine at 10-8 0.05). An ID50 value (dose which inhibits 50% of bFGF-induced neovascularisation) is calculated as 1 mg/kg. Low doses of Vinflunine reduce the number of experimental liver metastases by human LS174T colon cancer cell. A slight overall decrease in liver metastatic foci is already observed at the very low dose of 0.16 mg/kg Vinflunine, although maximal overall inhibition is reached at the maximal tolerated dose (MTD) of 20 mg/kg [3]. |
| Name | Vinflunine Tartrate |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Vinflunine Tartrat is a new vinca alkaloid uniquely fluorinated with the properties of mitotic-arresting and tubulin-interacting activity.Target: Microtubule/TubulinThe major effects of Vinflunine on dynamic instability are a slowing of the microtubule growth rate, an increase in growth duration, and a reduction in shortening duration. The effects of Vinflunine on the readmilling rate is examined by following [3H]GTP incorporation into MAP-rich microtubules, and the IC50 is 0.42 μM [1]. Vinflunine induced mitotic accumulation with IC50 with 18.8 nM, which decreases the centromere dynamicity by 44% and increases the time centromeres spent ina paused state by 63% [2]. Treatment of Vinflunine induces a rapid change in endothelial cell shape: cells retracts and assumes a rounded morphology. Mean IC50 values are 9.9 × 10-5 M × 10-5 M for fibronectin and 5.0× 10-5 M × 10-5 M for type IV collagen. A short 4 hours exposure of endothelial cells to Vinflunine at 10-8 0.05). An ID50 value (dose which inhibits 50% of bFGF-induced neovascularisation) is calculated as 1 mg/kg. Low doses of Vinflunine reduce the number of experimental liver metastases by human LS174T colon cancer cell. A slight overall decrease in liver metastatic foci is already observed at the very low dose of 0.16 mg/kg Vinflunine, although maximal overall inhibition is reached at the maximal tolerated dose (MTD) of 20 mg/kg [3]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| References |
| Molecular Formula | C49H60F2N4O14 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | 967.01600 |
| Exact Mass | 966.40700 |
| PSA | 248.93000 |
| LogP | 2.89690 |
| Storage condition | -20℃ |
| L-tartaric acid |
| S2209_Selleck |