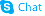74103-07-4
| Name | ketorolac tromethamine |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Ketorolac tromethamine
5-Benzoyl-2,3-dihydro-1H-pyrrolizine-1-carboxylic acid - 2-amino-2-(hydroxymethyl)propane-1,3-diol (1:1) 2-amino-2-(hydroxymethyl)propane-1,3-diol,5-benzoyl-2,3-dihydro-1H-pyrrolizine-1-carboxylic acid 5-(phenylcarbonyl)-2,3-dihydro-1H-pyrrolizine-1-carboxylic acid - 2-amino-2-(hydroxymethyl)propane-1,3-diol (1:1) 1H-Pyrrolizine-1-carboxylic acid, 5-benzoyl-2,3-dihydro-, compd. with 2-amino-2-(hydroxymethyl)-1,3-propanediol (1:1) Ketorolac tris salt rac Ketorolac Tromethamine Salt (±)-Ketorolac Tromethamine Salt MFCD00887595 5-(Phenylcarbonyl)-2,3-dihydro-1H-pyrrolizin-1-carbonsäure--2-amino-2-(hydroxymethyl)propan-1,3-diol(1:1) 5-Benzoyl-2,3-dihydro-1H-pyrrolizine-1-carboxylic acid - 2-amino-2-(hydroxymethyl)-1,3-propanediol (1:1) 1,3-Dihydroxy-2-(hydroxymethyl)propan-2-aminium 5-benzoyl-2,3-dihydro-1H-pyrrolizine-1-carboxylate Ketorolac (tromethamine salt) |
| Description | Ketorolac tromethamine salt is a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory agent, acting as a nonselective COX inhibitor, with IC50s of 20 nM for COX-1 and 120 nM for COX-2. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
COX-1:20 nM (IC50) COX-2:120 nM (IC50) |
| In Vitro | Ketorolac is a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory agent, acting as a nonselective COX inhibitor, with IC50s of 20 nM for COX-1 and 120 nM for COX-2[1]. |
| In Vivo | Ketorolac tromethamine (0.4%) causes nearly complete inhibition on LPS endotoxin-induced increases in FITC-dextran in the anterior chamber, and increases in aqueous PGE2 concentrations in the aqueous humor in rabbits[1].Ketorolac (30 mg/kg, i.v.) rapidly reverses hyperalgesia in rats. Ketorolac also reduces carrageenan-induced hyperalgesia and paw PG production, and causes reduction in PGE2 levels in rats[1]. Ketorolac (4 mg/kg/day, p.o.) has no detrimental effect in the volume fraction of bone trabeculae formed inside the alveolar socket in rats[2]. Ketorolac (60 μg/10 μL) reduces the histological changes such as ischemic cell death, including cytoplasmic eosinophilia with disintegration of cytoarchitecture and nuclear pyknosis in rats. Ketorolac also effectively reduces neuronal death and improves hindlimb motor function, and the long-term survival is similar to that in the control group[3]. |
| Animal Admin | Rats[2] Treated rats receive oral doses of 1 mL aqueous solution of paracetamol (80 mg/kg/rat/day), Ketorolac (4 mg/kg/day) or etoricoxib (10 mg/kg/day) administered by gavage from the day of surgery until death, 2 weeks later. Control rats receive tap water (1 mL/day by gavage). The animals are housed under climate-controlled environment (12 h light/12 h dark, 20-24ºC) with free access to standard laboratory chow and tap water[2]. |
| References |
| Boiling Point | 493.2ºC at 760 mmHg |
|---|---|
| Melting Point | 160-161ºC |
| Molecular Formula | C19H24N2O6 |
| Molecular Weight | 376.404 |
| Flash Point | 252.1ºC |
| Exact Mass | 376.163422 |
| PSA | 146.01000 |
| LogP | 0.65210 |
| Storage condition | Hygroscopic, Refrigerator, Under Inert Atmosphere |
| Water Solubility | H2O: 15 mg/mL stable at least one month at −20 °C., soluble |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| Symbol |

GHS06 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Danger |
| Hazard Statements | H301-H315-H319-H335 |
| Precautionary Statements | P261-P301 + P310-P305 + P351 + P338 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Faceshields;Gloves;type P2 (EN 143) respirator cartridges |
| Hazard Codes | T:Toxic |
| Risk Phrases | R25;R36/37/38 |
| Safety Phrases | S26-S45 |
| RIDADR | UN 2811 |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | UY7759900 |
| Packaging Group | II |
| Hazard Class | 6.1(a) |
| HS Code | 2942000000 |
| HS Code | 2942000000 |
|---|