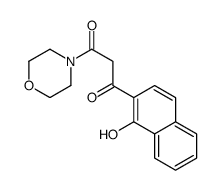
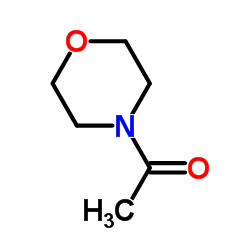
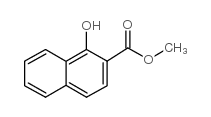
154447-35-5
| Name | 2-morpholin-4-ylbenzo[h]chromen-4-one |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
2-(Morpholin-4-yl)-benzo[h]chromen-4-one
NU7026 2-(4-Morpholinyl)-4H-benzo[h]chromen-4-one DNA-Dependent Protein Kinase Inhibitor II 2-(Morpholin-4-yl)-4H-benzo[h]chromen-4-one 4H-Naphtho[1,2-b]pyran-4-one, 2-(4-morpholinyl)- DNA-PK Inhibitor II 2-(morpholin-4-yl)benzo(h)chromen-4-one NU 7026 |
| Description | NU 7026 is a novel specific DNA-PK inhibitor with IC50 of 0.23±0.01 μM, also inhibits PI3K with IC50 of 13±3 μM. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
DNA-PK:0.23 μM (IC50) PI3K:13 μM (IC50) |
| In Vitro | NU7026 (10 μM) potentiates ionizing radiation (IR) cytotoxicity [potentiation factor at 90% cell kill (PF90)=1.51±0.04] in exponentially growing DNA-PK proficient but not deficient cells[1]. NU7026 synergistically sensitizes I83 cells to Chlorambucil (CLB) 3.5-fold[2].NU7026, a novel inhibitor of the DNA repair enzyme DNA-dependent protein kinase (DNA-PK). At a dose of 10 μM, which is nontoxic to cells per se, a minimum NU7026 exposure of 4 h in combination with 3 Gy radiation is required for a significant radiosensitisation effect in CH1 human ovarian cancer cells[3]. |
| In Vivo | NU7026, a novel inhibitor of the DNA repair enzyme DNA-dependent protein kinase (DNA-PK). Following intravenous administration to mice at 5 mg/kg, NU7026 underwent rapid plasma clearance (0.108 L/h) and this is largely attributed to extensive metabolism. Bioavailability following interperitoneal (i.p.) and p.o. administration at 20 mg/kg is 20 and 15%, respectively[3]. |
| Kinase Assay | Mammalian DNA-PK (500 ng/μL) is isolated from HeLa cell nuclear extract after chromatography using Q-Sepharose, S-Sepharose, and Heparin agarose. DNA-PK (250 ng) activity is measured at 30°C, in a final volume of 40 μL, in buffer containing 25 mM HEPES (pH 7.4), 12.5 mM MgCl2, 50 mM KCl, 1 mM DTT, 10% v/v Glycerol, 0.1% w/v NP-40, and 1 mg of the substrate GST-p53N66 (the NH2-terminal 66 amino acid residues of human wild-type p53 fused to glutathione S-transferase) in polypropylene 96-well plates. To the assay mix, varying concentrations of inhibitor (in DMSO at a final concentration of 1% v/v) are added. After 10 min of incubation, ATP is added to give a final concentration of 50 μM, along with a 30-mer double-stranded DNA oligonucleotide (final concentration of 0.5 ng/mL), to initiate the reaction. After 1 h with shaking, 150 μL of PBS are added to the reaction, and 5 μL are then transferred to a 96-well opaque white plate containing 45 μL of PBS per well, where the GSTp53N66 substrate is allowed to bind to the wells for 1 h. To detect the phosphorylation event on the serine 15 residue of p53 elicited by DNA-PK, a p53 phosphoserine-15 antibody is used in a basic ELISA procedure. An antirabbit horseradish peroxidase-conjugated secondary antibody is then used in the ELISA before the addition of chemiluminescence reagent to detect the signal as measured by chemiluminescent counting via a TopCount NXT[1]. |
| Cell Assay | I83 cells are plated in RPMI 1640 medium with 10% FBS (1.5×105 cells/mL) and treated with vehicle (DMSO), 5 μM CLB, CLB IC50, 10 μM NU7026, or the combination of both drugs for 0, 6, 24, and 48 h. Cell cycle distribution, apoptosis, DNA-PK phosphorylation, and γH2AX determination are determined, and they are expressed as a percentage of cells in each phase of the cycle. DNA content is analyzed with a FACSCalibur flow cytometer equipped with CellQuest software[2]. |
| Animal Admin | Mice[3] Female BALB/c mice are used. NU7026 is formulated in 10% DMSO and 5% Tween 20 in saline for i.p. and perorally (p.o.) administration at 20 and 50 mg/kg, respectively. For i.v. dosing at 5 mg/kg, NU7026 is formulated in 10% ethanol, 25% PEG 200 and 5% Tween 20 in saline. Control animals receive the vehicle alone. Groups of three mice are injected per time point. Blood is collected by cardiac puncture following transient anaesthesia with halothane at 0.083, 0.25, 0.5, 1, 2, 4, 6, and 24 h post administration. Following centrifugation at 1500 g for 2 min to obtain plasma, samples are stored at −20°C until analysis. For urinary excretion studies, NU7026 is administered at 5 mg/kg i.v. Urine is collected over 24 h in metabolic cages, and stored at −20°C until required. |
| References |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 459.9±45.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C17H15NO3 |
| Molecular Weight | 281.306 |
| Flash Point | 231.9±28.7 °C |
| Exact Mass | 281.105194 |
| PSA | 42.68000 |
| LogP | 3.29 |
| Appearance | solid | tan |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.1 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.673 |
| Storage condition | 2-8°C |
| Water Solubility | DMSO: 3 mg/mL at 60 °C, soluble |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Gloves;type N95 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter |
|---|---|
| Hazard Codes | Xi |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
|
~63% 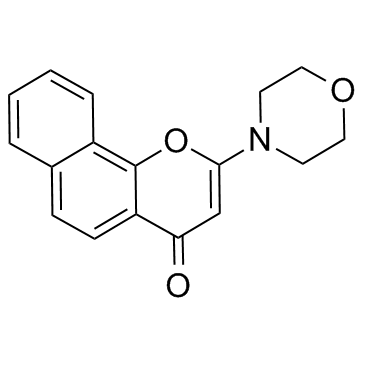
154447-35-5 |
| Literature: Griffin, Roger J.; Fontana, Gabriele; Golding, Bernard T.; Guiard, Sophie; Hardcastle, Ian R.; Leahy, Justin J. J.; Martin, Niall; Richardson, Caroline; Rigoreau, Laurent; Stockley, Martin; Smith, Graeme C. M. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, 2005 , vol. 48, # 2 p. 569 - 585 |
|
~% 
154447-35-5 |
| Literature: Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, , vol. 48, # 2 p. 569 - 585 |
|
~% 
154447-35-5 |
| Literature: Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, , vol. 48, # 2 p. 569 - 585 |
| Precursor 3 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 0 | |