Crotonyl-CoA
Modify Date: 2025-09-26 20:31:18
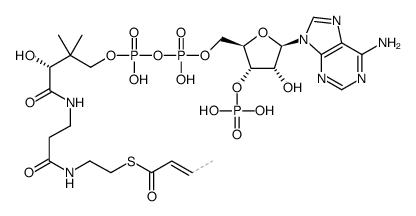
Crotonyl-CoA structure
|
Common Name | Crotonyl-CoA | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 992-67-6 | Molecular Weight | 835.60800 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C25H40N7O17P3S | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | N/A | |
Use of Crotonyl-CoACrotonyl-CoA is an intermediate in the fermentation of butyric acid, and in the metabolism of lysine and tryptophan. Crotonyl-CoA is important in the metabolism of fatty acids and amino acids[1]. |
| Name | but-2-enoyl-CoA |
|---|
| Description | Crotonyl-CoA is an intermediate in the fermentation of butyric acid, and in the metabolism of lysine and tryptophan. Crotonyl-CoA is important in the metabolism of fatty acids and amino acids[1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Human Endogenous Metabolite |
| References |
| Molecular Formula | C25H40N7O17P3S |
|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | 835.60800 |
| Exact Mass | 835.14100 |
| PSA | 418.36000 |
| LogP | 0.60380 |
| InChIKey | KFWWCMJSYSSPSK-PAXLJYGASA-N |
| SMILES | CC=CC(=O)SCCNC(=O)CCNC(=O)C(O)C(C)(C)COP(=O)(O)OP(=O)(O)OCC1OC(n2cnc3c(N)ncnc32)C(O)C1OP(=O)(O)O |