| Description |
Levobetaxolol is a potent and high affinity β-adrenergic antagonist with IC50 values of 33.2, 2970, 709 nM for guinea pig atrial β1, tracheal β2 and rat colonic β3 receptors, respectively. Levobetaxolol reduces IOP (intraocular pressure). Levobetaxolol exhibits a micromolar affinity for L-type Ca21-channels. Levobetaxolol decreases the effects of ischaemia/reperfusion injury in rats. Levobetaxolol has the potential for the research of glaucoma[1][2].
|
| Related Catalog |
|
| Target |
β1 adrenoceptor:33.2 nM (IC50)
β2 adrenoceptor:2970 nM (IC50)
β3 adrenoceptor:709 nM (IC50)
|
| In Vitro |
Levobetaxolol shows a higher affinity at cloned human β1 and β2 receptor with Ki values of 0.76, 32.6 nM, respectively[1]. Levobetaxolol inhibits functional activities in cells expressing human recombinant β1 and β2 receptors with Kb values of 6, 39 nM, respectively[1].
|
| References |
[1]. Sharif NA, et al. Levobetaxolol (Betaxon) and other beta-adrenergic antagonists: preclinical pharmacology, IOP-lowering activity and sites of action in human eyes. J Ocul Pharmacol Ther. 2001 Aug;17(4):305-17. [2]. Osborne NN, et al. Effectiveness of levobetaxolol and timolol at blunting retinal ischaemia is related to their calcium and sodium blocking activities: relevance to glaucoma. Brain Res Bull. 2004 Feb 15;62(6):525-8.
|
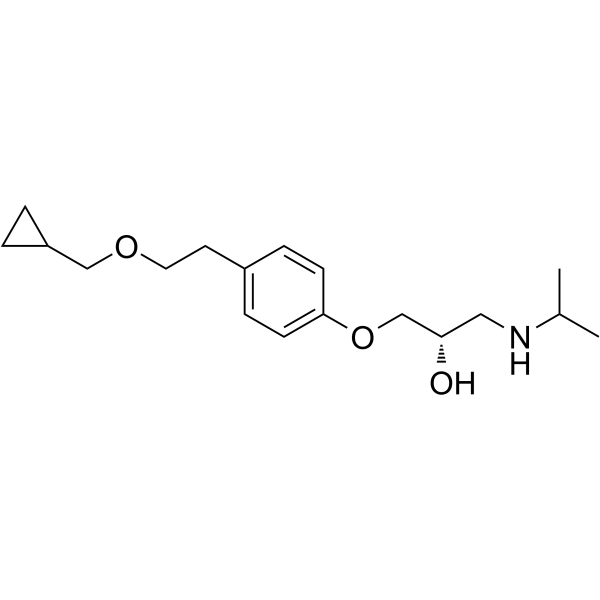
![S-(-)-1-{4-[2-(allyloxy)-ethyl]phenoxy}-3-isopropylamino propan-2-ol Structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/493/874112-86-4.png) CAS#:874112-86-4
CAS#:874112-86-4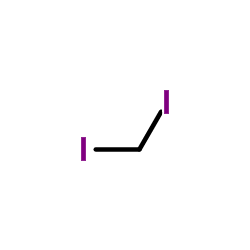 CAS#:75-11-6
CAS#:75-11-6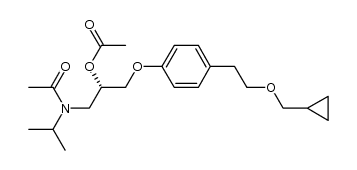 CAS#:169613-97-2
CAS#:169613-97-2![(S)-2-[4-(2-cyclopropylmethoxy ethyl)phenoxymethyl]oxirane Structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/114/874809-42-4.png) CAS#:874809-42-4
CAS#:874809-42-4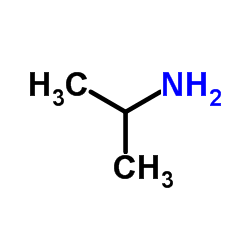 CAS#:75-31-0
CAS#:75-31-0 CAS#:63659-15-4
CAS#:63659-15-4 CAS#:61439-59-6
CAS#:61439-59-6 CAS#:56441-69-1
CAS#:56441-69-1 CAS#:501-94-0
CAS#:501-94-0 CAS#:104857-48-9
CAS#:104857-48-9