Crizotinib acetate
Modify Date: 2025-09-16 09:45:18
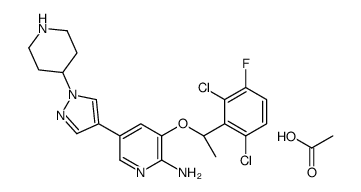
Crizotinib acetate structure
|
Common Name | Crizotinib acetate | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 877399-53-6 | Molecular Weight | 510.38900 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C23H26Cl2FN5O3 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | N/A | |
Use of Crizotinib acetateCrizotinib (PF-02341066) is an orally bioavailable, ATP-competitive ALK and c-Met inhibitor with IC50s of 20 and 8 nM, respectively. Crizotinib inhibits tyrosine phosphorylation of NPM-ALK and tyrosine phosphorylation of c-Met with IC50s of 24 and 11 nM in cell-based assays, respectively. Crizotinib is also a ROS1 inhibitor. Crizotinib has effective tumor growth inhibition[1][2][3]. |
| Name | acetic acid,3-[(1R)-1-(2,6-dichloro-3-fluorophenyl)ethoxy]-5-(1-piperidin-4-ylpyrazol-4-yl)pyridin-2-amine |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Crizotinib (PF-02341066) is an orally bioavailable, ATP-competitive ALK and c-Met inhibitor with IC50s of 20 and 8 nM, respectively. Crizotinib inhibits tyrosine phosphorylation of NPM-ALK and tyrosine phosphorylation of c-Met with IC50s of 24 and 11 nM in cell-based assays, respectively. Crizotinib is also a ROS1 inhibitor. Crizotinib has effective tumor growth inhibition[1][2][3]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| References |
| Molecular Formula | C23H26Cl2FN5O3 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | 510.38900 |
| Exact Mass | 509.14000 |
| PSA | 115.29000 |
| LogP | 6.03860 |
| Crizotinib acetate |