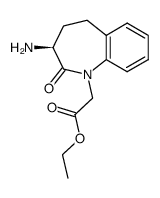
benazeprilat
Modify Date: 2025-08-27 22:01:10
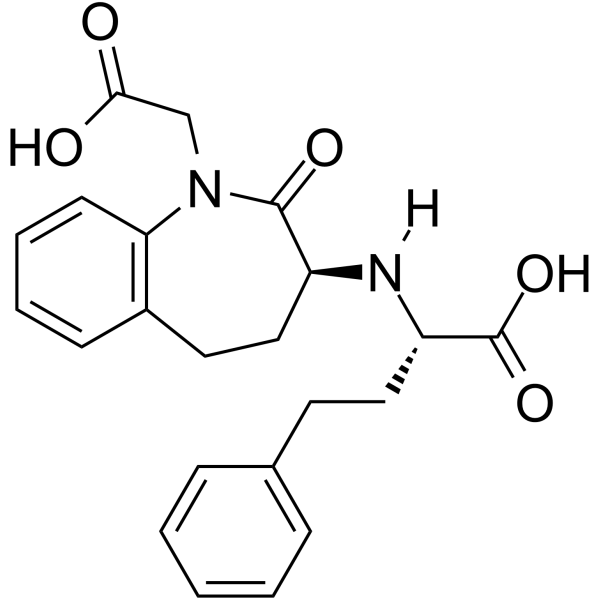
benazeprilat structure
|
Common Name | benazeprilat | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 86541-78-8 | Molecular Weight | 396.43600 | |
| Density | 1.34 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 711.3ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C22H24N2O5 | Melting Point | 270-272ºC | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | 384ºC | |
Use of benazeprilatBenazeprilat is an orally active and the active metabolite of benazepril, a carboxyl-containing ACE inhibitor with antihypertensive activity. Benazepril is a well-established antihypertensive agent, both in monotherapy and in combination with other classes of drugs including thiazide diuretics and calcium channel blockers. Benazepril is a first-line treatment in reducing various pathologies associated with CV risk and secondary end-organ damage[1][2][3]. |
| Name | benazeprilat |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Benazeprilat is an orally active and the active metabolite of benazepril, a carboxyl-containing ACE inhibitor with antihypertensive activity. Benazepril is a well-established antihypertensive agent, both in monotherapy and in combination with other classes of drugs including thiazide diuretics and calcium channel blockers. Benazepril is a first-line treatment in reducing various pathologies associated with CV risk and secondary end-organ damage[1][2][3]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Human Endogenous Metabolite |
| In Vivo | Benazeprilat (10 mg/kg, intravenous injection) and amlodipine (0.5 mg/kg, intravenous injection) in combination produce great hypotensive effect[2]. Benazepril (0.7 mg/kg, oral) markedly influences the dynamics of systemic RAAS peptides, resulting in a substantial decrease in AII and ALD while increasing PRA and AI[3]. Animal Model: Male SHR (14-16 weeks of age, 250-350 g)[2]. Dosage: 10 mg/kg Administration: I.V; once a day for 2 days. Result: Produced hypotensive effect. Animal Model: Beagle dogs (12.0-19.5 kg)[3]. Dosage: 0.7 mg/kg Administration: P.O, once a day for 5 days. Result: Effected systemic RAAS peptides. |
| References |
| Density | 1.34 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 711.3ºC at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 270-272ºC |
| Molecular Formula | C22H24N2O5 |
| Molecular Weight | 396.43600 |
| Flash Point | 384ºC |
| Exact Mass | 396.16900 |
| PSA | 106.94000 |
| LogP | 2.55050 |
| Index of Refraction | 1.643 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
|---|
| 1-carboxymethyl-3-1-carboxy-3-phenyl-(1S)-propylamino-2,3,4,5-tetrahydro-1H-(3S)-1-benzazepine-2-one |
| Cibacen |
| 3-[1-carboxy-3-phenyl-(1S)-propylamino]-2,3,4,5-tetrahydro-2-oxo-1H-1-(3S)-benzazepine-1-acetic acid |
| Benazepril Related Compound C (50 mg) ((3S)-3-[[(1S)-1- carboxy-3-phenylpropyl]amino-2,3,4,5-tetrahydro-2-oxo- 1H-1-benzazepine]-1-acetic acid) |
| benazeprilate |
| (3S)-3-[[(S)-1-Carboxy-3-phenylpropyl]amino]-2,3,4,5-tetrahydro-2-oxo-1H-1-benzazepine-1-acetic acid |
| (3S)-3-[[(1S)-1-carboxy-3-phenylpropyl]aMino-2,3,4,5-tetrahydro-2-oxo-1H-1-benzazepine]-1-acetic acid |
| 1H-1-Benzazepine-1-acetic acid,3-(1S)-1-carboxy-3-phenylpropylamino-2,3,4,5-tetrahydro-2-oxo-,(3S) |
| Benazepril Related CoMpound C |
| 1-carboxymethyl-3S-(1S-carboxy-3-phenylpropylamino)-2,3,4,5-tetrahydro-1H-[1]benzazepin-2-one |
![4,5-Dihydro-1H-benzo[b]azepin-2(3H)-one structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/098/4424-80-0.png)



![3-(S)-amino-1-ethoxycarbonylmethyl-2,3,4,5-tetrahydro-1H-[1]benzazepine-2-one structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/085/94793-89-2.png)