elpamotide
Modify Date: 2025-08-23 20:12:32
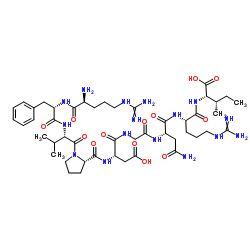
elpamotide structure
|
Common Name | elpamotide | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 673478-49-4 | Molecular Weight | 1073.206 | |
| Density | 1.5±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C47H76N16O13 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | N/A | |
Use of elpamotideElpamotide is an epitope peptide derived from VEGFR2. Elpamotide induces cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs) to kill VEGFR2-expressing endothelial cells. Elpamotide has potential immunostimulatory and antineoplastic activities. Elpamotide can be used in the research of cancer, such as pancreatic cancer[1][2]. |
| Name | elpamotide |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Elpamotide is an epitope peptide derived from VEGFR2. Elpamotide induces cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs) to kill VEGFR2-expressing endothelial cells. Elpamotide has potential immunostimulatory and antineoplastic activities. Elpamotide can be used in the research of cancer, such as pancreatic cancer[1][2]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | Elpamotide shows potent and specific cytotoxicity in cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs) (4-hour 51Cr-release assay) [1]. |
| Density | 1.5±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C47H76N16O13 |
| Molecular Weight | 1073.206 |
| Exact Mass | 1072.577759 |
| LogP | -0.97 |
| Index of Refraction | 1.661 |
| L-Isoleucine, L-arginyl-L-phenylalanyl-L-valyl-L-prolyl-L-α-aspartylglycyl-L-asparaginyl-L-arginyl- |
| S68632MB2G |
| L-Arginyl-L-phenylalanyl-L-valyl-L-prolyl-L-α-aspartylglycyl-L-asparaginyl-L-arginyl-L-isoleucine |
| 9318 |
| elpamotide |