2-Phospho-L-ascorbic acid trisodium salt
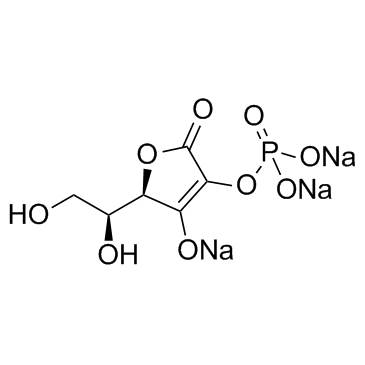
2-Phospho-L-ascorbic acid trisodium salt structure
|
Common Name | 2-Phospho-L-ascorbic acid trisodium salt | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 66170-10-3 | Molecular Weight | 322.049 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C6H6Na3O9P | Melting Point | 84 °C | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | N/A | |
Use of 2-Phospho-L-ascorbic acid trisodium salt2-Phospho-L-ascorbic acid trisodium salt acts as an antioxidant and a stimulator of hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) production. |
| Name | Sodium L-Ascorbyl-2-Phosphate |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | 2-Phospho-L-ascorbic acid trisodium salt acts as an antioxidant and a stimulator of hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) production. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | 2-Phospho-L-ascorbic acid (Asc 2-P) acts as an antioxidant and a stimulator of hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) production. 2-Phospho-L-ascorbic acid is a stable derivative of L-ascorbic acid (AA) and possesses similar biological properties as AA. AA and Asc-2P regulate a number of biological processes[1]. When 2-Phospho-L-ascorbic acid is added together with DHT, DHT-induced DKK-1 mRNA expression in DPCs is significantly attenuated. It is also found that DKK-1 promoter activity is increased by DHT treatmen. When 2-Phospho-L-ascorbic acid is added together with DHT, DHT-induced activation of luciferase activity is significantly repressed[2]. |
| References |
| Melting Point | 84 °C |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C6H6Na3O9P |
| Molecular Weight | 322.049 |
| Exact Mass | 321.944244 |
| PSA | 172.05000 |
| InChIKey | ABTBLEGNFLLCMG-OFBPEYICSA-N |
| SMILES | O=C1OC(C(O)CO)C(O)=C1OP(=O)(O)O.[Na].[Na].[Na] |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Gloves;type N95 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter |
|---|---|
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| HS Code | 2932209090 |
| HS Code | 2932209090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2932209090. other lactones. VAT:17.0%. Tax rebate rate:13.0%. . MFN tariff:6.5%. General tariff:20.0% |
|
High-sensitive electrochemical detection of point mutation based on polymerization-induced enzymatic amplification.
Biosens. Bioelectron. 26 , 3187-3191, (2011) Here a highly sensitive electrochemical method is described for the detection of point mutation in DNA. Polymerization extension reaction is applied to specifically initiate enzymatic electrochemical ... |
|
|
Design of experiments approach to engineer cell-secreted matrices for directing osteogenic differentiation.
Ann. Biomed. Eng. 39 , 1174-1185, (2011) The presentation of extracellular matrix (ECM) proteins provides an opportunity to instruct the phenotype and behavior of responsive cells. Decellularized cell-secreted matrix coatings (DM) represent ... |
|
|
Modulating and modeling aggregation of cell-seeded microcarriers in stirred culture system for macrotissue engineering.
J. Biotechnol. 150 , 438-446, (2010) A recently developed protocol, "microtissue assembly" holds great promise to address the issue of limited mass transfer within engineered large tissue replacements (macrotissues), wherein small "build... |
| Trisodium (5R)-5-[(1S)-1,2-dihydroxyethyl]-4-oxido-2-oxo-2,5-dihydro-3-furanyl phosphate |
| 2-Phospho-L-ascorbic acid trisodium salt |
| MFCD04038081 |

