1-Octacosanol
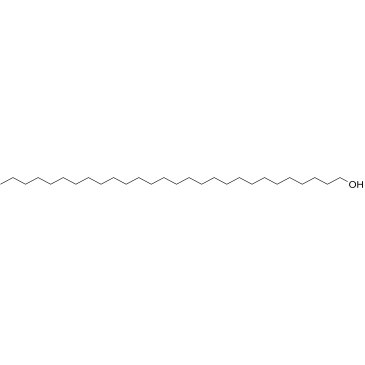
1-Octacosanol structure
|
Common Name | 1-Octacosanol | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 557-61-9 | Molecular Weight | 410.759 | |
| Density | 0.8±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 428.1±8.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C28H58O | Melting Point | 81-83°C | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 135.3±6.0 °C | |
Use of 1-Octacosanol1-Octacosanol is a straight-chain aliphatic 28-carbon fatty alcohol with well-known anti-fatigue function[1]. |
| Name | octacosan-1-ol |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | 1-Octacosanol is a straight-chain aliphatic 28-carbon fatty alcohol with well-known anti-fatigue function[1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| References |
| Density | 0.8±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 428.1±8.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 81-83°C |
| Molecular Formula | C28H58O |
| Molecular Weight | 410.759 |
| Flash Point | 135.3±6.0 °C |
| Exact Mass | 410.448761 |
| PSA | 20.23000 |
| LogP | 13.63 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±2.3 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.458 |
| InChIKey | CNNRPFQICPFDPO-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCO |
| Storage condition | 2-8°C |
| Stability | Stable. Light-sensitive. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. |
| Water Solubility | <0.1 g/100 mL at 21.5 ºC |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Gloves;type N95 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter |
|---|---|
| Hazard Codes | Xn |
| Risk Phrases | R20/21/22 |
| Safety Phrases | S22-S24/25 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | - |
| Packaging Group | I; II; III |
| HS Code | 2905199090 |
| Precursor 7 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 4 | |
| HS Code | 2905199090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2905199090. saturated monohydric alcohols. VAT:17.0%. Tax rebate rate:13.0%. . MFN tariff:5.5%. General tariff:30.0% |
|
In vitro and in vivo study of octacosanol metabolism.
Arch. Med. Res. 36(2) , 113-9, (2005) Policosanol is a mixture of very-long-chain aliphatic alcohols purified from sugar cane wax with cholesterol-lowering effects, whose main component is octacosanol. Scarce data about the metabolism of ... |
|
|
Galactolipids from Bauhinia racemosa as a new class of antifilarial agents against human lymphatic filarial parasite, Brugia malayi.
Eur. J. Med. Chem. 50 , 230-5, (2012) Bioassay guided fractionation of ethanolic extract of the leaves of Bauhinia racemosa led to the isolation of galactolipid and catechin class of the compounds (1-7) from the most active n-butanol frac... |
|
|
Contents and compositions of policosanols in green tea (Camellia sinensis) leaves.
Food Chem. 204 , 94-101, (2016) Policosanol (PC) is a mixture of health promoting bioactive long-chain aliphatic alcohols. Here, we report that green tea (Camellia sinensis) leaves are the exceptionally rich plant-sources of PC. You... |
| EINECS 209-181-2 |
| n-octacosanol |
| Octacosan-1-ol |
| 1-Octacosanol |
| MFCD00044770 |
| OCTACOSANOL,1 |
| octacosanol |
| Cluytyl alcohol |
| Policosanol |
| octacosyl alcohol |
 CAS#:636583-59-0
CAS#:636583-59-0 CAS#:17643-36-6
CAS#:17643-36-6 CAS#:112-89-0
CAS#:112-89-0 CAS#:6624-78-8
CAS#:6624-78-8 CAS#:55682-92-3
CAS#:55682-92-3 CAS#:505-95-3
CAS#:505-95-3 CAS#:73367-80-3
CAS#:73367-80-3 CAS#:506-48-9
CAS#:506-48-9 CAS#:4250-38-8
CAS#:4250-38-8 CAS#:18206-97-8
CAS#:18206-97-8 CAS#:16331-21-8
CAS#:16331-21-8
