Hyocholic Acid
Modify Date: 2025-08-22 08:00:10
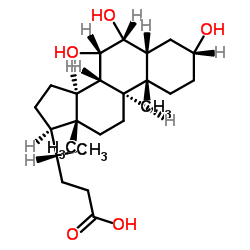
Hyocholic Acid structure
|
Common Name | Hyocholic Acid | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 547-75-1 | Molecular Weight | 408.571 | |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 565.7±40.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C24H40O5 | Melting Point | 188-189ºC | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | 310.0±23.8 °C | |
Use of Hyocholic AcidHyocholic Acid is a bile acid found in pig. Hyocholic Acid can also be found in urine samples from patients with cholestasis. Hyocholic Acid promotes GLP-1 secretion via activating TGR5 and inhibiting FXR in enteroendocrine cells. Hyocholic Acid is known for its exceptional resistance to type 2 diabetes [1][2][3]. |
| Name | hyocholic acid |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Hyocholic Acid is a bile acid found in pig. Hyocholic Acid can also be found in urine samples from patients with cholestasis. Hyocholic Acid promotes GLP-1 secretion via activating TGR5 and inhibiting FXR in enteroendocrine cells. Hyocholic Acid is known for its exceptional resistance to type 2 diabetes [1][2][3]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | HCA (25 and 50 μM, 24 h) upregulates GLP-1 protein secretion in STC-1 and NCI-H716 cells[3]. HCA (25 and 50 μM, 24 h) upregulates proglucagon gene transcription in STC-1 and NCI-H716 cells[3]. Western Blot Analysis[3] Cell Line: NCI-H716 cells Concentration: 50 μM Incubation Time: 48 h Result: Inhibited the high expression of SHP (small heterodimer partner) induced by the FXR agonist. |
| In Vivo | Hyocholic Acid (20 mg/kg, p.o.) suppresses BA depletion-induced blood glucose increase in pigs[3]. Hyocholic Acid (100 mg/kg/day, p.o.) improves serum fasting GLP-1 secretion and glucose homeostasis in diabetic mouse models[3]. Animal Model: BA depletion pigs[3] Dosage: 20 mg/kg Administration: Oral administration (p.o.) Result: Attenuated the increased blood glucose levels corresponding with GLP-1 decrease. Animal Model: db/db model, and the high-fat diet and streptozotocin (HFD+STZ) induced diabetic model[3] Dosage: 100 mg/kg/day Administration: Oral administration (p.o.) Result: Improved oral glucose tolerances shown by lower glucose levels. Increased circulating active GLP-1 levels and fasting insulin levels. |
| References |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 565.7±40.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 188-189ºC |
| Molecular Formula | C24H40O5 |
| Molecular Weight | 408.571 |
| Flash Point | 310.0±23.8 °C |
| Exact Mass | 408.287567 |
| PSA | 97.99000 |
| LogP | 3.82 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±3.5 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.558 |
| Precursor 7 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 4 | |
| 3Alpha,6Alpha,7Alpha-Trihydroxy-5Beta-cholanic Acid |
| Hyocholic Acid |
| Cholan-24-oic acid, 3,6,7-trihydroxy-, (3α,5β,6α,7α)- |
| (3α,5β,6α,7α)-3,6,7-Trihydroxycholan-24-oic acid |
| 3a,6a,7a-Trihydroxy-5b-cholan-24-oic acid |
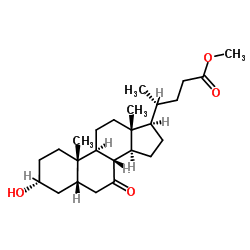 CAS#:10538-59-7
CAS#:10538-59-7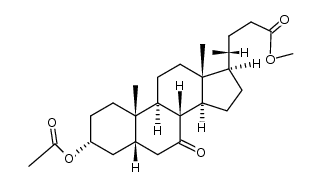 CAS#:10452-65-0
CAS#:10452-65-0 CAS#:3057-04-3
CAS#:3057-04-3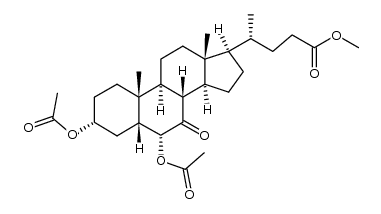 CAS#:108760-45-8
CAS#:108760-45-8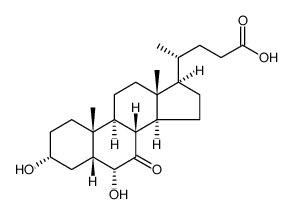 CAS#:88725-42-2
CAS#:88725-42-2 CAS#:4651-67-6
CAS#:4651-67-6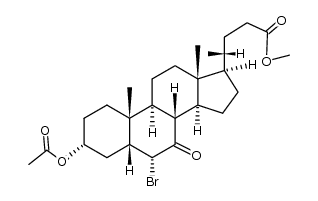 CAS#:10452-64-9
CAS#:10452-64-9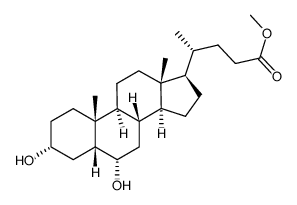 CAS#:2868-48-6
CAS#:2868-48-6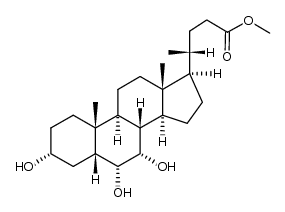 CAS#:10190-22-4
CAS#:10190-22-4 CAS#:2862-62-6
CAS#:2862-62-6