Prostaglandin D2
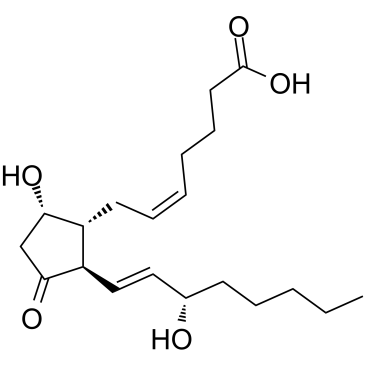
Prostaglandin D2 structure
|
Common Name | Prostaglandin D2 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 41598-07-6 | Molecular Weight | 352.465 | |
| Density | 1.1±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 549.6±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C20H32O5 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 300.3±26.6 °C | |
| Symbol |


GHS07, GHS08 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
Use of Prostaglandin D2Prostaglandin D2 (PGD2) is one of the major PGs actively produced in the brain of various mammals[1]. Prostaglandin D2 is one of the most potent endogenous sleep promoting substances[2]. PGD2 plays a protective role by suppressing inflammation[3]. |
| Name | prostaglandin D2 |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Prostaglandin D2 (PGD2) is one of the major PGs actively produced in the brain of various mammals[1]. Prostaglandin D2 is one of the most potent endogenous sleep promoting substances[2]. PGD2 plays a protective role by suppressing inflammation[3]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Human Endogenous Metabolite |
| In Vivo | Prostaglandin D2 (PGD2; infused into the lateral ventricle; 5-50 pmol/min; for 6 hours between 20:00 and 2:00) induces sleep-wake profiles in A2AR KO mice[2]. Animal Model: Male WT and A2AR KO mice of the inbred C57BL/6 strain (weighing 23-27 g, 11-13 weeks old)[1] Dosage: 5, 10, 20, or 50 pmol/min Administration: Infused into the lateral ventricle; for 6 hours between 20:00 and 2:00 Result: Induced sleep-wake profiles. |
| References |
[1]. Suzuki F, et al. Transport of prostaglandin D2 into brain. Brain Res. 1986 Oct 22;385(2):321-8. |
| Density | 1.1±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 549.6±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C20H32O5 |
| Molecular Weight | 352.465 |
| Flash Point | 300.3±26.6 °C |
| Exact Mass | 352.224976 |
| PSA | 94.83000 |
| LogP | 2.02 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±3.4 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.561 |
| Storage condition | 20°C |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
MUTATION DATA
|
| Symbol |


GHS07, GHS08 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Danger |
| Hazard Statements | H302-H360 |
| Precautionary Statements | P201-P308 + P313 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;full-face particle respirator type N100 (US);Gloves;respirator cartridge type N100 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter;type P3 (EN 143) respirator cartridges |
| Hazard Codes | T: Toxic; |
| Risk Phrases | 60-22 |
| Safety Phrases | S22;S26;S36;S53 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| RTECS | UK7930000 |
|
HMDB: a knowledgebase for the human metabolome.
Nucleic Acids Res. 37(Database issue) , D603-10, (2009) The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB, http://www.hmdb.ca) is a richly annotated resource that is designed to address the broad needs of biochemists, clinical chemists, physicians, medical geneticists, ... |
|
|
The human serum metabolome.
PLoS ONE 6(2) , e16957, (2011) Continuing improvements in analytical technology along with an increased interest in performing comprehensive, quantitative metabolic profiling, is leading to increased interest pressures within the m... |
|
|
Malva sylvestris L. extract suppresses desferrioxamine-induced PGE₂ and PGD₂ release in differentiated U937 cells: the development and validation of an LC-MS/MS method for prostaglandin quantification.
Biomed. Chromatogr. 28(7) , 986-93, (2014) Malva sylvestris is a species used worldwide as an alternative to anti-inflammatory therapies; however, its mechanism of action remains unknown. In this paper, the anti-inflammatory effects of M. sylv... |
| PGD2 |
| (5Z,9α,13E,15S)-9,15-Dihydroxy-11-oxoprosta-5,13-dien-1-oic acid |
| Prosta-5,13-dien-1-oic acid, 9,15-dihydroxy-11-oxo-, (5Z,9α,13E,15S)- |
| Prostaglandin D2 |
| (5Z,9α,13E,15S)-9,15-dihydroxy-11-oxo-prosta-5,13-dien-1-oic acid |
| MFCD00077857 |
![(5Z,13E)-9α-[(tert-butyldimethylsilyl)oxy]-11-oxo-15-[(tert-butyldiphenylsilyl)oxy]prosta-5,13-dienoic acid Structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/087/101249-10-9.png) CAS#:101249-10-9
CAS#:101249-10-9 CAS#:61305-35-9
CAS#:61305-35-9 CAS#:85800-97-1
CAS#:85800-97-1 CAS#:72522-67-9
CAS#:72522-67-9 CAS#:62410-84-8
CAS#:62410-84-8