Caudatin
Modify Date: 2025-08-21 17:04:51
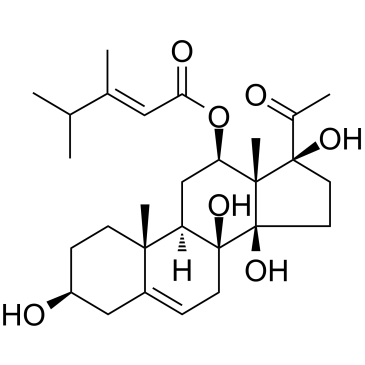
Caudatin structure
|
Common Name | Caudatin | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 38395-02-7 | Molecular Weight | 490.629 | |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 617.9±55.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C28H42O7 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | 197.5±25.0 °C | |
Use of CaudatinCaudatin is a steroidal cmpound found in Cynanchum auriculatum, causes cell cycle arrest and induces apoptosis, with anti-cancer and antiangiogenic properties[1]. |
| Name | Caudatin |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Caudatin is a steroidal cmpound found in Cynanchum auriculatum, causes cell cycle arrest and induces apoptosis, with anti-cancer and antiangiogenic properties[1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| References |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 617.9±55.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C28H42O7 |
| Molecular Weight | 490.629 |
| Flash Point | 197.5±25.0 °C |
| Exact Mass | 490.293060 |
| PSA | 124.29000 |
| LogP | 4.37 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±4.1 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.584 |
| Storage condition | 2-8C |
| 2-Pentenoic acid, 3,4-dimethyl-, (3β,12β,14β)-3,8,14,17-tetrahydroxy-20-oxopregn-5-en-12-yl ester, (2E)- |
| (3β,12β,14β)-3,8,14,17-Tetrahydroxy-20-oxopregn-5-en-12-yl (2E)-3,4-dimethyl-2-pentenoate |

