JA-ACC
Modify Date: 2025-09-18 19:03:37
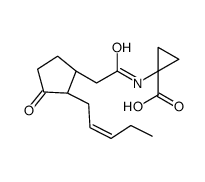
JA-ACC structure
|
Common Name | JA-ACC | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 371778-55-1 | Molecular Weight | 293.35800 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C16H23NO4 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | N/A | |
Use of JA-ACCJA-ACC (Jasmonyl-ACC) is a derivative of 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylic acid (ACC). ACC is the direct precursor of the plant hormone ethylene. JA-ACC inhibits root growth in Arabidopsis and the inhibition is independent of jasmonic acid (JA) signaling[1]. |
| Name | 1-[[2-[(1R,2R)-3-oxo-2-[(Z)-pent-2-enyl]cyclopentyl]acetyl]amino]cyclopropane-1-carboxylic acid |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | JA-ACC (Jasmonyl-ACC) is a derivative of 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylic acid (ACC). ACC is the direct precursor of the plant hormone ethylene. JA-ACC inhibits root growth in Arabidopsis and the inhibition is independent of jasmonic acid (JA) signaling[1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | JA-ACC (Jasmonyl-ACC) serves as a pivotal molecule which can function as a modulator of the hormonal cross-talk between the ethylene and jasmonic acid pathway[1]. JA-ACC is the second most abundant JA conjugate detected in Arabidopsis leaves and is formed by JAR1, a JA-amino synthetase[2]. |
| References |
| Molecular Formula | C16H23NO4 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | 293.35800 |
| Exact Mass | 293.16300 |
| PSA | 86.96000 |
| LogP | 2.90180 |
| jasmonic acid / 1-amino-1-cyclopropane carboxylic acid |
| N-[(3R,7R)-()-Jasmonoyl]-aminocyclopropane carboxylic acid |
| cyclopropanecarboxylic acid,1-[[[(1R,2R)-3-oxo-2-[(2Z)-2-pentenyl]cyclopentyl]acetyl]amino] |
| Cyclopropanecarboxylic acid,1-[[[3-oxo-2-(2Z)-2-pentenylcyclopentyl]acetyl]amino]-(9CI) |