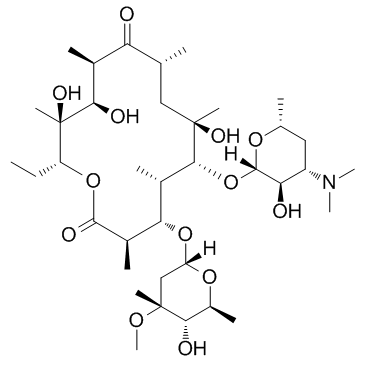
Erythromycin Estolate

Erythromycin Estolate structure
|
Common Name | Erythromycin Estolate | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 3521-62-8 | Molecular Weight | 1000.324 | |
| Density | 1.0053 (rough estimate) | Boiling Point | 827.7ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C52H97NO18S | Melting Point | 135-140ºC dec. | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 454.4ºC | |
| Symbol |


GHS07, GHS08 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
Use of Erythromycin EstolateErythromycin estolate, erythromycin derivative[1], is a macrolide antibiotic used in the treatment of a wide variety of bacterial infections. Erythromycin estolate causes several cases of liver injury which mostly include cholestatic hepatitis. Erythromycin estolate toxicity is related to its inhibitory effect on bile acid transport[2]. |
| Name | erythromycin estolate |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Erythromycin estolate, erythromycin derivative[1], is a macrolide antibiotic used in the treatment of a wide variety of bacterial infections. Erythromycin estolate causes several cases of liver injury which mostly include cholestatic hepatitis. Erythromycin estolate toxicity is related to its inhibitory effect on bile acid transport[2]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| References |
| Density | 1.0053 (rough estimate) |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 827.7ºC at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 135-140ºC dec. |
| Molecular Formula | C52H97NO18S |
| Molecular Weight | 1000.324 |
| Flash Point | 454.4ºC |
| Exact Mass | 999.616394 |
| PSA | 271.96000 |
| LogP | 7.55400 |
| Index of Refraction | 1.6550 (estimate) |
| Storage condition | -20°C Freezer |
| Water Solubility | chloroform: soluble4.0ML, clear, colorless (200 mg + 4.0 mL Chloroform) |
|
Section 1. Chemical Product and Company Identification Erythromycin Estolate Common Name/ Trade Name Erythromycin Estolate Section 3. Hazards Identification Slightly hazardous in case of skin contact (irritant), of eye contact (irritant), of ingestion, of inhalation.
Potential Acute Health Effects CARCINOGENIC EFFECTS: Not available. Potential Chronic Health MUTAGENIC EFFECTS: Not available. Effects TERATOGENIC EFFECTS: Not available. DEVELOPMENTAL TOXICITY: Not available. The substance may be toxic to liver. Repeated or prolonged exposure to the substance can produce target organs damage. Section 4. First Aid Measures Check for and remove any contact lenses. In case of contact, immediately flush eyes with plenty of water for at least Eye Contact 15 minutes. Get medical attention if irritation occurs. Wash with soap and water. Cover the irritated skin with an emollient. Get medical attention if irritation develops. Skin Contact Not available. Serious Skin Contact InhalationIf inhaled, remove to fresh air. If not breathing, give artificial respiration. If breathing is difficult, give oxygen. Get medical attention. Serious InhalationNot available. Do NOT induce vomiting unless directed to do so by medical personnel. Never give anything by mouth to an Ingestion unconscious person. If large quantities of this material are swallowed, call a physician immediately. Loosen tight clothing such as a collar, tie, belt or waistband. Not available. Serious Ingestion Section 5. Fire and Explosion Data Flammability of the Product May be combustible at high temperature. Auto-Ignition Temperature Not available. Not available. Flash Points Not available. Flammable Limits These products are carbon oxides (CO, CO2), nitrogen oxides (NO, NO2...). Products of Combustion Fire Hazards in Presence of Slightly flammable to flammable in presence of heat. Various Substances Risks of explosion of the product in presence of mechanical impact: Not available. Explosion Hazards in Risks of explosion of the product in presence of static discharge: Not available. Presence of Various Substances SMALL FIRE: Use DRY chemical powder. Fire Fighting Media LARGE FIRE: Use water spray, fog or foam. Do not use water jet. and Instructions Material in powder form, capable of creating a dust explosion. As with most organic solids, fire is possible at elevated Special Remarks on temperatures Fire Hazards Fine dust dispersed in air in sufficient concentrations, and in the presence of an ignition source is a potential dust Special Remarks on explosion hazard. Explosion Hazards Erythromycin Estolate Section 6. Accidental Release Measures Use appropriate tools to put the spilled solid in a convenient waste disposal container. Finish cleaning by spreading Small Spill water on the contaminated surface and dispose of according to local and regional authority requirements. Use a shovel to put the material into a convenient waste disposal container. Finish cleaning by spreading water on Large Spill the contaminated surface and allow to evacuate through the sanitary system. Section 7. Handling and Storage Keep away from heat. Keep away from sources of ignition. Ground all equipment containing material. Do not Precautions ingest. Do not breathe dust. Wear suitable protective clothing. If ingested, seek medical advice immediately and show the container or the label. Keep container tightly closed. Keep container in a cool, well-ventilated area. Storage Section 8. Exposure Controls/Personal Protection Use process enclosures, local exhaust ventilation, or other engineering controls to keep airborne levels below Engineering Controls recommended exposure limits. If user operations generate dust, fume or mist, use ventilation to keep exposure to airborne contaminants below the exposure limit. Personal ProtectionSafety glasses. Lab coat. Dust respirator. Be sure to use an approved/certified respirator or equivalent. Gloves. Personal Protection in Case Splash goggles. Full suit. Dust respirator. Boots. Gloves. A self contained breathing apparatus should be used to avoid inhalation of the product. Suggested protective clothing might not be sufficient; consult a specialist BEFORE of a Large Spill handling this product. Exposure LimitsNot available. Section 9. Physical and Chemical Properties Solid. (Crystalline powder.)Odorless. Physical state andO dor appearance Not available. Taste 1056.39 g/mole Molecular Weight White. Color Not applicable. pH (1% soln/water) Not available. Boiling Point Decomposition temperature: 135°C (275°F) - 140 C. Melting Point Not available. Critical Temperature Not available. Specific Gravity Not applicable. Vapor Pressure Not available. Vapor Density Not available. Volatility Not available. Odor Threshold Not available. Water/Oil Dist. Coeff. Not available. Ionicity (in Water) Not available. Dispersion Properties Insoluble in cold water. Solubility Erythromycin Estolate Section 10. Stability and Reactivity Data The product is stable. Stability Not available. Instability Temperature Conditions of Instability Excess heat, dust generation Incompatibility with various Not available. substances Not available. Corrosivity Not available. Special Remarks on Reactivity Not available. Special Remarks on Corrosivity Will not occur. Polymerization Section 11. Toxicological Information Inhalation. Ingestion. Routes of Entry Acute oral toxicity (LD50): 1447 mg/kg [Rat]. Toxicity to Animals Chronic Effects on Humans May cause damage to the following organs: liver. Other Toxic Effects onSlightly hazardous in case of skin contact (irritant), of ingestion, of inhalation. Humans Not available. Special Remarks on Toxicity to Animals May cause adverse reproductive effects. Special Remarks on Chronic Effects on Humans Special Remarks on otherAcute Potential Health Effects: Toxic Effects on HumansSkin: May cause skin irritation. Eyes: May cause eye irritation. Inhalation: May cause respiratory tract irritation. Ingestion: May cause nausea, vomiting, abdominal cramps, diarrhea. May affect the liver. May cause hearing loss. Chronic Potential Health Effects: Ingestion: May cause symtoms similar to acute ingestion. May cause weight loss. May affect the liver. Medical Conditions Aggravated by Exposure: Hypersensitivity to material; impaired liver function; hearing loss; history of cardiac arrhythmias or QT prolongation. Section 12. Ecological Information Not available. Ecotoxicity Not available. BOD5 and COD Products of Biodegradation Possibly hazardous short term degradation products are not likely. However, long term degradation products may arise. The products of degradation are less toxic than the product itself. Toxicity of the Products of Biodegradation Not available. Special Remarks on the Products of Biodegradation Erythromycin Estolate Section 13. Disposal Considerations Waste must be disposed of in accordance with federal, state and local environmental control Waste Disposal regulations. Section 14. Transport Information Not a DOT controlled material (United States). DO T Cl assi fi cati on Not applicable. Identification Not applicable. Special Provisions for Transport DO T (Pi ctograms) Section 15. Other Regulatory Information and Pictograms No products were found. Federal and State Regulations California prop. 65: This product contains the following ingredients for which the State of California has found to California cause cancer which would require a warning under the statute: No products were found. Proposition 65 Warnings California prop. 65: This product contains the following ingredients for which the State of California has found to cause birth defects which would require a warning under the statute: No products were found. Other RegulationsEINECS: This product is on the European Inventory of Existing Commercial Chemical Substances (EINECS No. 222-532-4). Canada: Not listed on Canadian Domestic Substance List (DSL) or Candian Non-Domestic Substances List (NDSL) China: Not listed on National Inventory. Japan: Not listed on National Inventory (ENCS). Korea: Listed on National Inventory (KECI). Philippines: Not listed on National Inventory (PICCS). Australia: Listed on AICS. WHMIS (Canada) Not controlled under WHMIS (Canada). Other Classifications R22- Harmful if swallowed.S46- If swallowed, seek medical advice DSCL (EEC) immediately and show this container or label. Health Hazard HMIS (U.S.A.)1 National Fire Protection 1 Flammability 1 Association (U.S.A.) Fire Hazard 1 0 Reactivity Health Reactivity0 Specific hazard Personal Protection E WHMIS (Canada) (Pictograms) DSCL (Europe) (Pictograms) Erythromycin Estolate TDG(Canada) (Pictograms) ADR (Europe) (Pictograms) Protective Equipment Gloves. Lab coat. Dust respirator. Be sure to use an approved/certified respirator or equivalent. SECTION 16 - ADDITIONAL INFORMATION N/A |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| Symbol |


GHS07, GHS08 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Danger |
| Hazard Statements | H302-H317-H334 |
| Precautionary Statements | P261-P280-P342 + P311 |
| Hazard Codes | Xn:Harmful |
| Risk Phrases | R22;R42/43 |
| Safety Phrases | S22-S36 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | KF5775000 |
| HS Code | 29419000 |
|
~% 
Erythromycin Es... CAS#:3521-62-8 |
| Literature: Skin Pharmacology, , vol. 8, # 6 p. 319 - 325 |
| Precursor 2 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 0 | |
|
Protective effect of Livex, a herbal formulation against erythromycin estolate induced hepatotoxicity in rats.
J. Ethnopharmacol. 57(3) , 161-7, (1997) Livex, a compound herbal formulation, was investigated for its possible hepatoprotective effect in Wistar rats against erythromycin estolate induced toxicity. Oral administration of Livex significantl... |
|
|
Preparation and characterization of biodegradable poly(l-lactide)/poly(ethylene glycol) microcapsules containing erythromycin by emulsion solvent evaporation technique.
J. Colloid. Interface Sci. 271(2) , 336-41, (2004) In this work, the producing of a biodegradable poly(l-lactide) (PLA)/poly(ethylene glycol) (PEG) microcapsule by emulsion solvent evaporation method was investigated. The effect of PEG segments added ... |
|
|
Pharmacokinetics of erythromycin estolate and erythromycin phosphate after intragastric administration to healthy foals.
Am. J. Vet. Res. 61(8) , 914-9, (2000) To determine pharmacokinetics and plasma concentrations of erythromycin and related compounds after intragastric administration of erythromycin phosphate and erythromycin estolate to healthy foals.11 ... |
| Erythromycin Estolate |
| Erythromycin 2'-propionate dodecyl sulfate |
| Erythromycin 2′-propionate dodecyl sulfate |
| Dodecyl hydrogen sulfate - (3R,4S,5S,6R,7R,9R,11R,12R,13S,14R)-6-{[(2S,3R,4S,6R)-4-(dimethylamino)-3-hydroxy-6-methyltetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl]oxy}-14-ethyl-7,12,13-trihydroxy-4-{[(2R,4R,5S,6S)-5-hydroxy-4-methoxy-4,6-dimethyltetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl]oxy}-3,5,7,9,11,13-hexamethyloxacyclotetradecane-2,10-dione (1:1) |
| Erythromycin 2-Propionate Dodecyl Sulfate |