69-23-8 (free base)
Modify Date: 2025-08-25 08:44:53
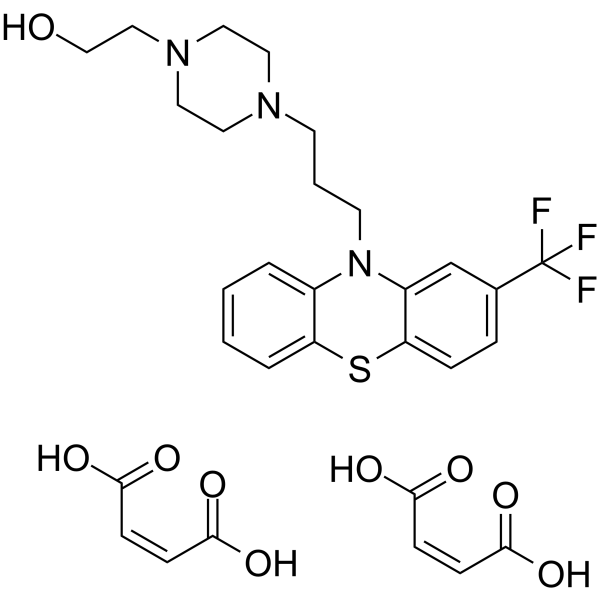
69-23-8 (free base) structure
|
Common Name | 69-23-8 (free base) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 3093-66-1 | Molecular Weight | 553.59400 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C26H30F3N3O5S | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | N/A | |
Use of 69-23-8 (free base)Fluphenazine dimaleate is a potent, orally active phenothiazine-based dopamine receptor antagonist. Fluphenazine dimaleate blocks neuronal voltage-gated sodium channels. Fluphenazine dimaleate acts primarily through antagonism of postsynaptic dopamine-2 receptors in mesolimbic, nigrostriatal, and tuberoinfundibular neural pathways. Fluphenazine dimaleate can antagonize Methylphenidate-induced stereotyped gnawing and inhibit climbing behaviour in mice. Fluphenazine dimaleate can be used for researching psychosis and painful peripheral neuropathy associated with diabetes and has potential to inhibit SARS-CoV-2[1][2][3][4][6]. |
| Name | fluphenazine dimaleate |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Fluphenazine dimaleate is a potent, orally active phenothiazine-based dopamine receptor antagonist. Fluphenazine dimaleate blocks neuronal voltage-gated sodium channels. Fluphenazine dimaleate acts primarily through antagonism of postsynaptic dopamine-2 receptors in mesolimbic, nigrostriatal, and tuberoinfundibular neural pathways. Fluphenazine dimaleate can antagonize Methylphenidate-induced stereotyped gnawing and inhibit climbing behaviour in mice. Fluphenazine dimaleate can be used for researching psychosis and painful peripheral neuropathy associated with diabetes and has potential to inhibit SARS-CoV-2[1][2][3][4][6]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Dopamine receptor, Sodium channels, SARS-CoV-2[1][2] |
| In Vivo | Fluphenazine (1 mg/kg; IG, treated from day 6 to day 15 of gestation) causes malformations in pregnant mice[5]. Fluphenazine (0.125-1 mg/kg; IP, single dosage) antagonizes Methylphenidate-induced stereotyped gnawing; inhibits significantly climbing behaviour[6]. Animal Model: Mature female Swiss-Webster mice[5] Dosage: 1 mg/kg Administration: IG, treated from day 6 to day 15 of gestation Result: Significantly reduced fetal weight and length, increased the incidence of incomplete ossification of sternebrae and skull bones. Animal Model: Mice (injected with 60 mg/kg Methylphenidate)[6] Dosage: 0.125, 0.25, 0.5, and 1 mg/kg Administration: IP, single dosage Result: Antagonized Methylphenidate-induced stereotyped gnawing; inhibited significantly climbing behaviour in mice at 0.0625-0.5 mg/kg, and at the dose of 1 mg/kg abolished this effect completely. |
| References |
| Molecular Formula | C26H30F3N3O5S |
|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | 553.59400 |
| Exact Mass | 553.18600 |
| PSA | 129.85000 |
| LogP | 3.96070 |
| InChIKey | GTJLCONXCUYJOF-SPIKMXEPSA-N |
| SMILES | O=C(O)C=CC(=O)O.O=C(O)C=CC(=O)O.OCCN1CCN(CCCN2c3ccccc3Sc3ccc(C(F)(F)F)cc32)CC1 |
| Risk Phrases | 20/21/22-36/37/38 |
|---|---|
| Safety Phrases | 26-36 |
| RIDADR | UN 3249 |
| fluphenazine dimaleate salt |
| MFCD00679032 |