(E)-Astringin
Modify Date: 2025-08-25 17:02:30
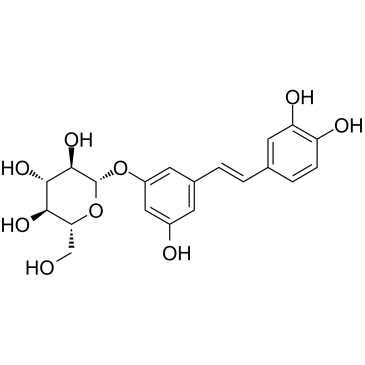
(E)-Astringin structure
|
Common Name | (E)-Astringin | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 29884-49-9 | Molecular Weight | 406.38300 | |
| Density | 1.593±0.06 g/cm3(Predicted) | Boiling Point | 756.1±60.0 °C(Predicted) | |
| Molecular Formula | C20H22O9 | Melting Point | 218-220 °C | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | N/A | |
Use of (E)-AstringinAstringin (trans-Astringin) is a natural glycoside found in the bark of Picea sitchensis and Picea abies (Norway spruce), in Vitis vinifera cell cultures and in wine. Astringin has potent antioxidant capacity and cancer-chemopreventive activity[1]. |
| Name | trans-astringin |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Astringin (trans-Astringin) is a natural glycoside found in the bark of Picea sitchensis and Picea abies (Norway spruce), in Vitis vinifera cell cultures and in wine. Astringin has potent antioxidant capacity and cancer-chemopreventive activity[1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| References |
| Density | 1.593±0.06 g/cm3(Predicted) |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 756.1±60.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Melting Point | 218-220 °C |
| Molecular Formula | C20H22O9 |
| Molecular Weight | 406.38300 |
| Exact Mass | 406.12600 |
| PSA | 160.07000 |
| LogP | 0.15250 |
| Vapour Pressure | 5.06E-24mmHg at 25°C |
| (E)-Astringin |
| Astringin |
| (2S,3R,4S,5S,6R)-2-[3-[(E)-2-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)ethenyl]-5-hydroxyphenoxy]-6-(hydroxymethyl)oxane-3,4,5-triol |

