Orientin
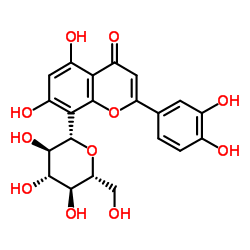
Orientin structure
|
Common Name | Orientin | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 28608-75-5 | Molecular Weight | 448.377 | |
| Density | 1.8±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 816.1±65.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C21H20O11 | Melting Point | 260-285ºC | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 289.1±27.8 °C | |
Use of OrientinOrientin is a naturally occurring bioactive flavonoid that possesses diverse biological properties, including anti-inflammation, anti-oxidative, anti-tumor, and cardio protection. Orientin is a promising neuroprotective agent suitable for therapy for neuropathic pain[1][2]. |
| Name | Orientine |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Orientin is a naturally occurring bioactive flavonoid that possesses diverse biological properties, including anti-inflammation, anti-oxidative, anti-tumor, and cardio protection. Orientin is a promising neuroprotective agent suitable for therapy for neuropathic pain[1][2]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| References |
| Density | 1.8±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 816.1±65.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 260-285ºC |
| Molecular Formula | C21H20O11 |
| Molecular Weight | 448.377 |
| Flash Point | 289.1±27.8 °C |
| Exact Mass | 448.100555 |
| PSA | 201.28000 |
| LogP | 1.58 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±3.1 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.767 |
| InChIKey | PLAPMLGJVGLZOV-VPRICQMDSA-N |
| SMILES | O=c1cc(-c2ccc(O)c(O)c2)oc2c(C3OC(CO)C(O)C(O)C3O)c(O)cc(O)c12 |
| Storage condition | 2~8°C |
| Water Solubility | 1 M NaOH: soluble1mg/mL, clear, yellow-orange |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATAMUTATION DATA
|
|
Distinction of the C-glycosylflavone isomer pairs orientin/isoorientin and vitexin/isovitexin using HPLC-MS exact mass measurement and in-source CID.
Phytochem. Anal. 16(5) , 295-301, (2005) HPLC-MS using collision induced dissociation (CID) has been utilised for the identification of the C-glycosylflavone isomer pairs orientin/isoorientin and vitexin/isovitexin. HPLC-CID/MS analyses prod... |
|
|
Antihypertensive and cardioprotective effects of the Lagenaria siceraria fruit in NG-nitro-L-arginine methyl ester (L-NAME) induced hypertensive rats.
Pharm. Biol. 50(11) , 1428-35, (2012) Lagenaria siceraria (Molina) Standl. (Cucurbitacae) (LS) has been reported to possess cardioprotective, antihyperlipidemic, and diuretic activities.To evaluate antihypertensive and cardioprotective ef... |
|
|
Development and validation of an HPTLC method for simultaneous quantitation of isoorientin, isovitexin, orientin, and vitexin in bamboo-leaf flavonoids.
J. AOAC Int. 93(5) , 1376-83, (2010) A simple HPTLC method has been developed for the simultaneous determination of isoorientin, isovitexin, orientin, and vitexin, both pure and in commercial samples of bamboo-leaf flavonoids. The flavon... |
| isoorientin |
| (1S)-1,5-Anhydro-1-[2-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-5,7-dihydroxy-4-oxo-4H-chromen-8-yl]-D-glucitol |
| 2-(3,4-Dihydroxyphényl)-5,7-dihydroxy-8-[(2S,3R,4R,5S,6R)-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-(hydroxyméthyl)tétrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl]-4H-chromén-4-one |
| Orientin 8-C-β-D-glucopyranoside |
| 3',4',5,7-tetrahydroxyflavone-8-C-glucoside |
| 2-(3,4-Dihydroxyphenyl)-5,7-dihydroxy-8-[(2S,3R,4R,5S,6R)-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)tetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl]-4H-chromen-4-on |
| Luteolin-8-C-glucoside |
| 3',4',5,7-tetrahydroxyflavone 8-glucoside |
| 4H-1-Benzopyran-4-one, 2-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-8-β-D-glucopyranosyl-5,7-dihydroxy- |
| D-Glucitol, 1,5-anhydro-1-C-[2-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-5,7-dihydroxy-4-oxo-4H-1-benzopyran-8-yl]-, (1S)- |
| Orientin |
| lutexin |
| 2-(3,4-Dihydroxyphenyl)-5,7-dihydroxy-8-[(2S,3R,4R,5S,6R)-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)tetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl]-4H-chromen-4-one |
| 2-(3,4-Dihydroxyphenyl)-8-b-D-glucopyranosyl-5,7-dihydroxy-4H-1-benzopyran-4-one |

