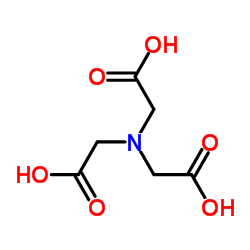
ADA
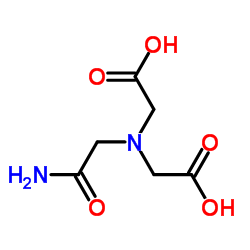
ADA structure
|
Common Name | ADA | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 26239-55-4 | Molecular Weight | 190.154 | |
| Density | 1.5±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 524.9±45.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C6H10N2O5 | Melting Point | 219 °C (dec.)(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 271.3±28.7 °C | |
Use of ADAADA is a biological buffer[1]. ADA can serve as a chelator[2]. |
| Name | 2,2'-[(2-amino-2-oxoethyl)imino]diacetic acid |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | ADA is a biological buffer[1]. ADA can serve as a chelator[2]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| References |
| Density | 1.5±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 524.9±45.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 219 °C (dec.)(lit.) |
| Molecular Formula | C6H10N2O5 |
| Molecular Weight | 190.154 |
| Flash Point | 271.3±28.7 °C |
| Exact Mass | 190.058975 |
| PSA | 120.93000 |
| LogP | -1.29 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±3.0 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.558 |
| Storage condition | Store at RT. |
| Water Solubility | soluble |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Gloves;type N95 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter |
|---|---|
| Safety Phrases | S24/25 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| HS Code | 29241900 |
|
~31% 
ADA CAS#:26239-55-4 |
| Literature: Mancilla, Teresa; Carrillo, Lourdes; De La Paz Reducindo Polyhedron, 1996 , vol. 15, # 21 p. 3777 - 3785 |
|
~% 
ADA CAS#:26239-55-4 |
| Literature: Voronkov,M.G.; Mikhailova,S.V. Zhurnal Organicheskoi Khimii, 1971 , vol. 7, p. 1616 - 1618,1678 - 1680 |
| Precursor 2 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 0 | |
| HS Code | 2924199090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2924199090. other acyclic amides (including acyclic carbamates) and their derivatives; salts thereof. VAT:17.0%. Tax rebate rate:13.0%. . MFN tariff:6.5%. General tariff:30.0% |
|
Effect of hyperoxic and hyperbaric conditions on the adenosinergic pathway and CD26 expression in rat.
J. Appl. Physiol. 119 , 140-7, (2015) The nucleoside adenosine acts on the nervous and cardiovascular systems via the A2A receptor (A2AR). In response to oxygen level in tissues, adenosine plasma concentration is regulated in particular v... |
|
|
Adenosine A2AR blockade prevents neuroinflammation-induced death of retinal ganglion cells caused by elevated pressure.
J. Neuroinflammation 12 , 115, (2015) Elevated intraocular pressure (IOP) is a major risk factor for glaucoma, a degenerative disease characterized by the loss of retinal ganglion cells (RGCs). There is clinical and experimental evidence ... |
|
|
Chemotherapeutic agents attenuate CXCL12-mediated migration of colon cancer cells by selecting for CXCR4-negative cells and increasing peptidase CD26.
BMC Cancer 15 , 882, (2015) Recurrence of colorectal cancer (CRC) may arise due to the persistence of drug-resistant and cancer-initiating cells that survive exposure to chemotherapy. Proteins responsible for this recurrence inc... |
| N-(2-Acetamido)iminodiacetic acid (ADA) |
| 2,2'-[(2-Amino-2-oxoethyl)imino]diacetic acid |
| N-(2-Acetamido)imidodiacetic acid |
| Acetic acid, 2,2'-[(2-amino-2-oxoethyl)imino]bis- |
| N-carbamoyl methyl aminodiacetic acid |
| 2-[(2-amino-2-oxoethyl)-(carboxymethyl)amino]acetic acid |
| 2,2'-((2-Amino-2-oxoethyl)azanediyl)diacetic acid |
| Carbamoylmethylaminodiacetic acid |
| MFCD00008031 |
| N-(2-Acetamido)iminodiacetic acid (N-(Carbamoylmethyl)iminodiacetic acid |
| N-(2-acetamido)-iminodiacetic acid |
| N-(2-Acetamido)Iminodiacetic Acid |
| N-(Carbamoylmethyl)iminodiacetic acid |
| ADA |
| N-(2-amino-2-oxoethyl)-N-(carboxymethyl)glycine |
| EINECS 247-530-0 |
| 2,2′-[(2-amino-2-oxoethyl)imino]diacetic acid |
![(N->B)phenyl[N-carbamoylmethyl-aminodiacetate-O,O',N]borane structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/307/181523-90-0.png)